Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, my brilliant student! How are you today? Have you ever seen a plant’s leaves curl up or its stomata close when the weather is hot and dry? That’s the work of a special plant hormone called Abscisic Acid (ABA)! This hormone acts as a stress signal, helping plants survive drought by controlling water loss and other protective mechanisms. Today, we’ll learn about the role of ABA in drought response and how it helps plants cope with water shortages.
Role of Abscisic Acid (ABA) in Drought Response
What is Abscisic Acid (ABA)?
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that plays a key role in stress responses, especially during drought. It helps plants reduce water loss, close stomata, and survive harsh conditions. Think of ABA as the plant’s emergency alarm system—it quickly reacts when the plant is under drought stress.
How ABA Helps Plants Respond to Drought
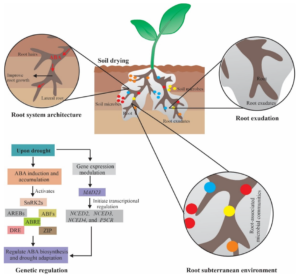
When a plant experiences water shortage, ABA levels increase in the leaves and roots. This triggers several drought survival strategies:
Stomatal Closure – Reducing Water Loss
ABA signals guard cells to close the stomata, preventing excess water loss through transpiration.
This helps the plant conserve moisture during dry conditions.
Root Growth Enhancement – Searching for Water
ABA stimulates root growth, especially deep roots, so the plant can find water underground.
At the same time, it slows down shoot growth to reduce water usage.
Leaf Responses – Curling and Shedding
Some plants curl their leaves to reduce exposure to sunlight and minimise evaporation.
In extreme drought, ABA may trigger leaf shedding (abscission) to reduce water loss further.
Production of Drought-Protective Proteins
ABA helps plants produce special proteins that protect cells from dehydration.
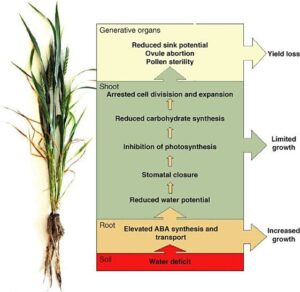
These proteins help the plant recover quickly when water becomes available again.
Real-Life Example of ABA in Action
Imagine you are in the hot sun without water. Your body starts conserving sweat to prevent dehydration. Similarly, when a plant faces drought, ABA acts like an emergency signal, telling the plant to close stomata, slow growth, and preserve water until conditions improve.
Why is ABA Important for Plants?
Prevents Excessive Water Loss – By closing stomata, ABA helps plants survive dry conditions.
Encourages Deeper Root Growth – Helps the plant access underground water.
Triggers Drought-Protective Mechanisms – Produces proteins that protect plant cells.
Increases Survival in Harsh Environments – Helps plants recover quickly after drought.
Summary
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is a stress hormone that helps plants survive drought by:
Closing stomata to reduce water loss.
Promoting deep root growth to access underground water.
Curling or shedding leaves to conserve moisture.
Producing protective proteins that prevent dehydration.
Evaluation
- What is Abscisic Acid (ABA), and why is it important?
- How does ABA help a plant survive during drought?
- Why do plants close their stomata when ABA levels increase?
- What happens to root growth when ABA is activated?
Excellent work! Now you know how plants use ABA to survive when water is scarce. Keep up the great learning with Afrilearn—science is fun and exciting when you understand how nature works! See you in the next lesson!
