Back to: Botany 100 Level
Hello, my brilliant Afrilearn scholar! Have you ever seen the fence and gate around a house? They protect the home, allow visitors in, and keep unwanted guests out. Similarly, plant cells have a plasma membrane that acts like a security gate, controlling what enters and leaves the cell. Inside the cell, everything is well-organised, just like a well-arranged living room. This organisation within the cytoplasm helps the cell function properly.
Today, we’ll learn about the plasma membrane and cytoplasmic organisation in plant cells and why they are essential for plant life!
Plasma Membrane And Cytoplasmic Organization In Plant Cells
What is the Plasma Membrane?
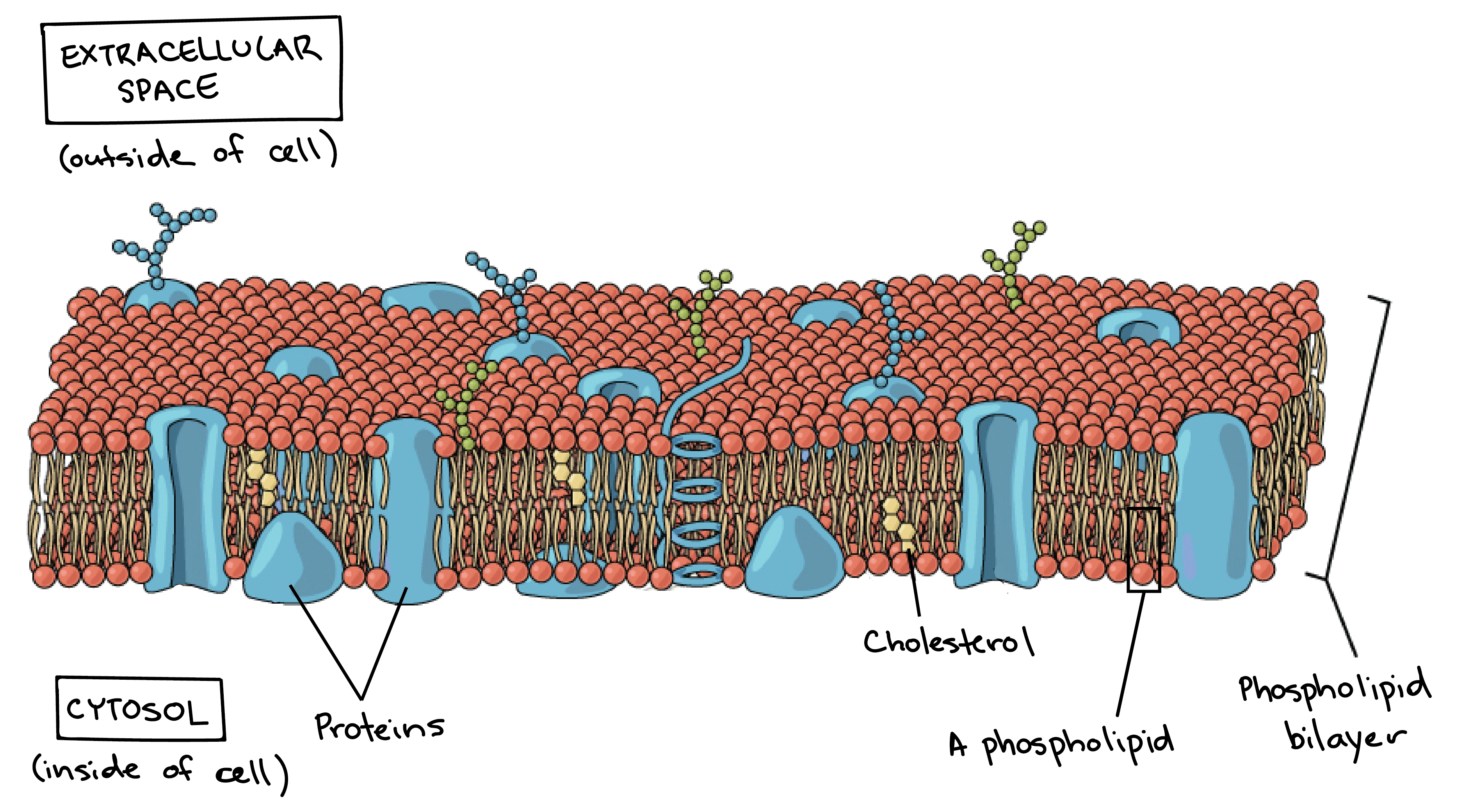
The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell. Unlike the cell wall, which is rigid and strong, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable—meaning it allows some substances to pass while blocking others.

Structure of the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer (two layers of fat molecules) along with proteins and carbohydrates. Imagine a sandwich:
The bread layers represent phospholipids (which form the main structure of the membrane).
The fillings represent proteins and carbohydrates, which help in transport and communication.
The membrane is described as a fluid mosaic model, meaning it is flexible and has different components that move within it.
Functions of the Plasma Membrane

1. Controls Entry and Exit of Substances
The plasma membrane acts as a gatekeeper, allowing essential substances (like water, oxygen, and nutrients) to enter while removing waste products.
2. Protects the Cell
It prevents harmful substances from entering, just like a security fence protects a house.
3. Communication and Signal Reception
Proteins in the membrane help cells communicate with each other by receiving and sending signals.
4. Maintains Internal Balance (Homeostasis)
The plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances to keep conditions inside the cell stable.
What is Cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is the gel-like fluid that fills the cell. It is made up of water, salts, and organic molecules and contains all the organelles (tiny cell structures that perform different functions).
Think of cytoplasm as the space inside a house, where different rooms (organelles) are arranged to serve different purposes.
Organisation of the Cytoplasm in Plant Cells
The cytoplasm is well-organised to ensure that materials move efficiently and that all organelles function properly. It consists of:
Cytosol – The liquid part of the cytoplasm where chemical reactions take place.
Organelles – Tiny structures that perform specific tasks.
Cytoskeleton – A network of protein fibres that helps maintain the shape of the cell and supports movement.
Key Organelles in the Cytoplasm
Nucleus – The control centre that contains DNA.
Mitochondria – The powerhouse of the cell, providing energy.
Chloroplasts – Found in plant cells, they help in photosynthesis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – A transport system for proteins and lipids.
Golgi Apparatus – Packages and distributes proteins.
Vacuole – Stores water, food, and waste.
All these organelles float in the cytoplasm and work together to keep the cell alive.
Why Are the Plasma Membrane and Cytoplasmic Organisation Important?
Without the plasma membrane, a plant cell would not be able to control what goes in and out, leading to damage or death. Without proper cytoplasmic organisation, the cell would be a chaotic mess, making it impossible for organelles to function effectively.
Together, the plasma membrane and cytoplasmic organisation ensure that the cell:
Gets the nutrients it needs
Removes waste efficiently
Communicates with other cells
Maintains its shape and structure
Summary
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the plant cell, controlling what enters and exits.
It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and carbohydrates.
The cytoplasm is the fluid inside the cell that contains organelles and supports their functions.
Organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts work inside the cytoplasm to keep the cell alive.
The cytoskeleton helps in maintaining the cell’s shape and movement.
Evaluation
- What is the main function of the plasma membrane?
- Why is the plasma membrane called selectively permeable?
- What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol?
- Name two organelles found in the cytoplasm and their functions.
- How does the cytoskeleton help plant cells?
You are learning so much! Cells may be small, but they are amazingly organised to function efficiently. Keep up your great work, and see you in the next lesson!
