Back to: Botany 100 Level
Hello, my brilliant Afrilearn scholar! Have you ever wondered what happens to the food plants make during photosynthesis? Imagine you cook a pot of jollof rice. Do you just leave it in the pot, or do you eat it to get energy? Just like we eat food to get energy, plants also break down the glucose they make to release energy. This process is called cellular respiration.
Today, we’ll learn about cellular respiration in plant cells—what it is, where it happens, and why it’s important. Let’s get started!
Cellular Respiration In Plant Cells
What Is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which plants break down glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) to release energy (ATP) for growth and survival.
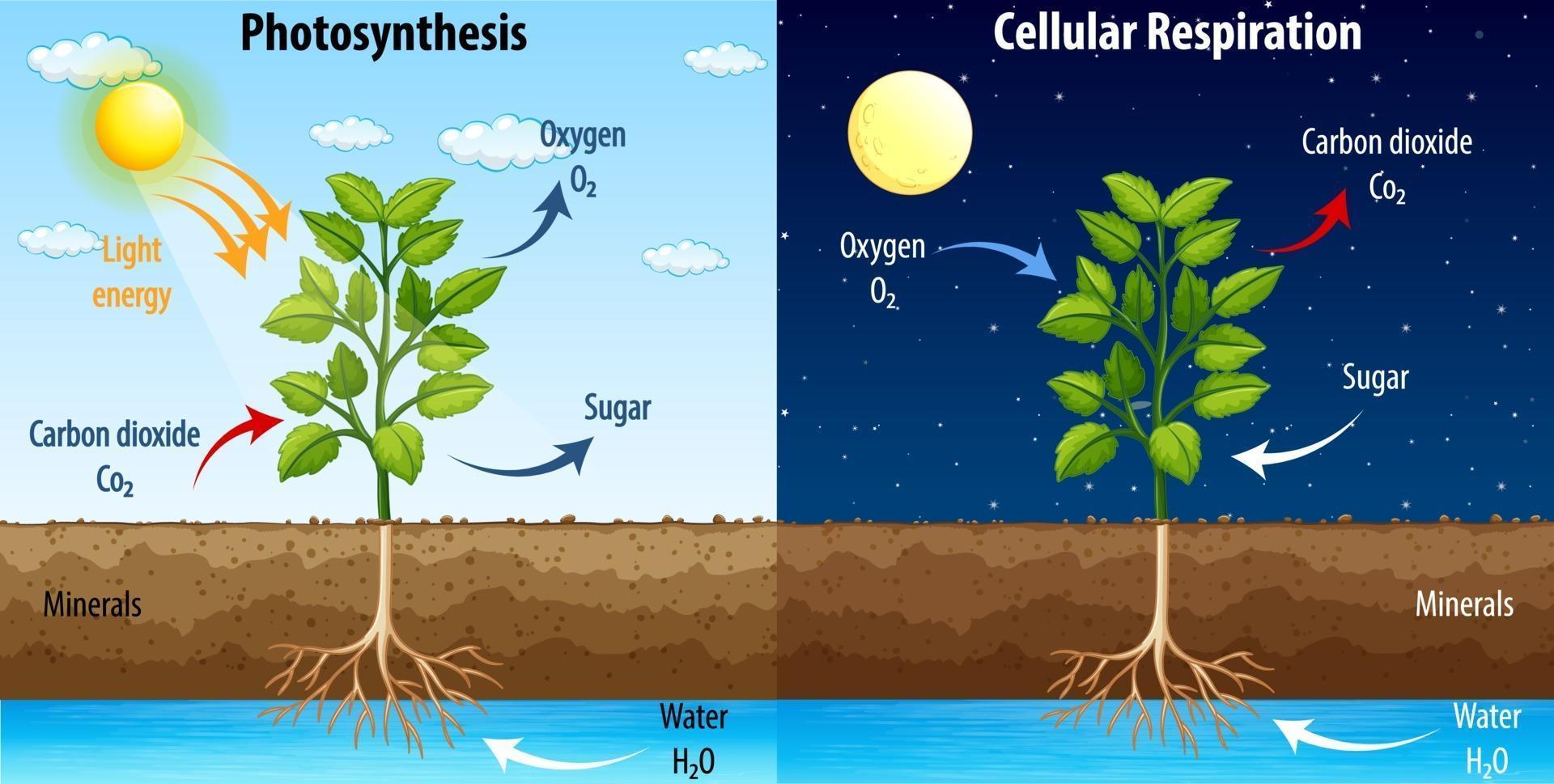
While photosynthesis stores energy by making glucose, cellular respiration releases energy by breaking down glucose. The energy released is stored in a special molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)—the “battery” that powers plant cells.
The equation for cellular respiration is:
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+ATP(energy)C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP (energy)
This means plants take in glucose and oxygen, break them down, and release carbon dioxide, water, and energy (ATP).
Where Does Cellular Respiration Happen?
Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria—the “powerhouse” of the cell. The mitochondria take glucose and oxygen and turn them into ATP.
Stages of Cellular Respiration
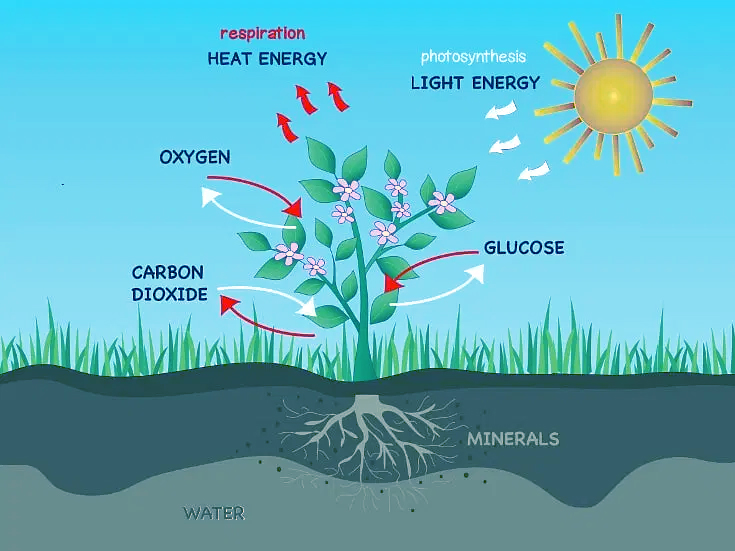
Cellular respiration happens in three main stages:
Glycolysis (Happens in the Cytoplasm)
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) (Happens in the Mitochondria)
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) (Happens in the Mitochondria)
1. Glycolysis (Breaking Down Glucose in the Cytoplasm)
The first step happens in the cytoplasm of the cell.
The glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is broken down into two smaller molecules of pyruvate.
This step produces a small amount of ATP.
No oxygen is needed yet (this means glycolysis can happen even in low-oxygen conditions).
2. Krebs Cycle (Energy Extraction in the Mitochondria)
The pyruvate molecules move into the mitochondria.
Oxygen is used to break them down further.
This releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) and produces more ATP and high-energy molecules (NADH & FADH₂).
3. Electron Transport Chain (ATP Production in the Mitochondria)
This is the final and most important step.
The high-energy molecules from the Krebs Cycle pass their energy through a chain of proteins inside the mitochondria.
This produces a large amount of ATP—the energy needed by the plant to grow and function.
Oxygen is needed, and water (H₂O) is released as a byproduct.
Types of Cellular Respiration
There are two types of cellular respiration:
Aerobic Respiration (With Oxygen)
Uses oxygen.
Produces a large amount of ATP (energy).
Releases CO₂ and H₂O as byproducts.
Happens in most plants.
Anaerobic Respiration (Without Oxygen)
Does not use oxygen.
Produces less ATP.
In some cases, produces alcohol or lactic acid as byproducts.
Some microorganisms and plants (e.g., waterlogged roots) use this process.
Why Is Cellular Respiration Important for Plants?
Cellular respiration is very important because:
It provides energy for growth. Without ATP, plants can’t grow or make new leaves, roots, or flowers.
It powers all plant functions. Energy from respiration helps in photosynthesis, nutrient absorption, and repair of damaged cells.
It balances photosynthesis. While photosynthesis stores energy, respiration releases it so the plant can use it.
Even at night when photosynthesis stops, cellular respiration continues to provide energy for the plant!
Summary
Cellular respiration is the process by which plants break down glucose to release energy (ATP).
It happens in three stages:
Glycolysis (in the cytoplasm) – Glucose is broken down into smaller molecules.
Krebs Cycle (in the mitochondria) – More ATP and energy carriers are produced.
Electron Transport Chain (in the mitochondria) – The most ATP is produced.
There are two types of respiration:
Aerobic respiration (with oxygen, produces more ATP).
Anaerobic respiration (without oxygen, produces less ATP).
Cellular respiration is essential for plant survival, providing energy for growth, repair, and function.
Evaluation Activities
- What is the main purpose of cellular respiration?
- Which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration?
- What are the three stages of cellular respiration?
- How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
- Why do plants need cellular respiration even though they carry out photosynthesis?
You are doing an amazing job! Now you understand how plants use the food they make to get energy! Keep up your great learning, and see you in the next lesson!

