Back to: ZOOLOGY 100 Level
My person! Welcome again to another lovely Afrilearn class. How market today? Hope say your energy dey high like NEPA when dem no take light? Today’s lesson na very important one because it go help you understand wetin really dey go on inside living things—both plants and animals. You fit chop leaf soup and goat meat, but do you know what makes their cells different? Oya, let’s gist small.
Comparison of animal and plant cells
Think of a compound with two buildings—one na flat where humans dey live, the other na poultry where chickens dey stay. Both buildings get rooms, doors and windows, but dem still different in design and use. That’s how animal and plant cells be—similar in some ways, but different in others.
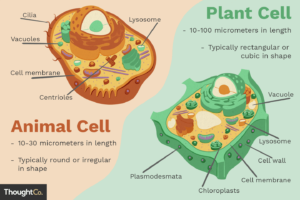
Whether you’re looking at a mango tree or your neighbour’s dog, they’re both living things. But when you look inside with microscope eyes (imagine say you get super eyes like that), you go see that their cells—those small living units—are not exactly the same. Today, we go understand how animal and plant cells resemble, and how dem differ.
Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a nucleus and other organelles (small organs) enclosed in membranes. But beyond that, they get some unique differences.
Let’s break it down.
Similarities Between Animal and Plant Cells:
- Nucleus – Both have a nucleus that controls the activities of the cell, like the oga at the top.
- Cytoplasm – This is the jelly-like substance where the cell’s activities happen, like market activity inside cell.
- Cell Membrane – A soft barrier that controls what goes in and out—like your house gate.
- Mitochondria – The powerhouse of the cell; it produces energy for work—like your generator when NEPA no show.
Ribosomes – These are the workers that produce protein—think of them like pepper grinders in mama put shop.
Imagine you pluck a leaf from an orange tree and take a cheek cell from your mouth (gently o!). Under the microscope, the leaf cell will show green structures—chloroplasts—that help it make food from sunlight. Your cheek cell no get that, because you no fit photosynthesise (na food you must chop).
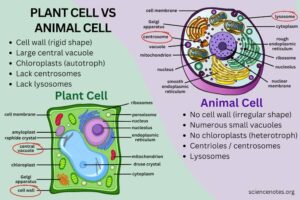
The plant cell go look like a well-arranged compound with a big fence (cell wall), big tank (vacuole), and solar panel (chloroplasts). But your animal cell be like open compound—flexible wall, smaller water tank, and no solar panel. Na you dey buy fuel (food), not make am.
Summary
Animal and plant cells share basic parts like the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and cell membrane. But plant cells have extras like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole, which make them unique. These differences allow plants to make their own food and stay strong, while animals depend on feeding and movement.
Evaluation
- Mention three similarities between animal and plant cells.
- List three features that are found only in plant cells.
- Why can’t animal cells perform photosynthesis?
You really dey burst brain today! You’ve shown great understanding, and you’re becoming a proper African scientist with sharp eyes for details. Keep asking questions, keep learning. With Afrilearn, the sky is just your starting point. Until next class—stay curious and confident, because greatness dey your DNA!
