Back to: ZOOLOGY 100 Level
I’m so glad to have you here today! How are you doing? I hope you’re feeling strong, curious and ready to learn something new and exciting. Today, we’re going to have a really interesting time learning about the four major types of animal tissues. Don’t worry—it won’t be too technical. We’ll keep it simple, just like we’re chatting under the mango tree on a sunny afternoon. So, grab your notes, settle down and let’s begin our learning journey together!
Epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues
We all know how important a house’s structure is, right? Imagine your body like a house. Every house has walls, pipes, wiring, and support beams, and they all serve different functions. In the same way, our body is made up of different tissues that work together to help us grow, move, feel, and survive. The main ones we’ll focus on are epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
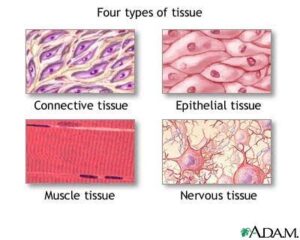
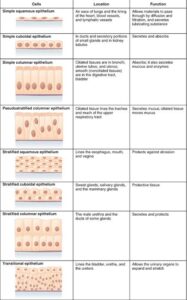
Let’s begin with epithelial tissue. Think of this like the protective covering or skin of your body, and even the inner lining of organs. Just like how a wrapper protects food, epithelial tissue covers and lines every surface of your body. It helps with protection, absorption (like when your intestines absorb food), secretion (like sweat from your skin), and even sensation. You’ll find epithelial tissue in places like your skin, your nose, your mouth, and even your stomach lining.
Now to connective tissue—this one is like the cement or the glue of the body. It connects, supports, and holds everything together. Some common examples are blood (yes, blood is a connective tissue), bone, fat, and cartilage. If you think of a football team, connective tissue is like the coach—it organises everything and makes sure all the players (body parts) are working well together. Imagine the cartilage in your ears or knees—it gives shape and cushion. Or think of fat tissue—it stores energy and keeps us warm.
Next up is muscular tissue. As the name suggests, this is what helps us move. Whether you’re dancing at a wedding, running to catch a bus, or even just blinking, your muscular tissues are hard at work. There are three types: skeletal muscles (which help with movement), smooth muscles (which are in organs like your stomach and help with digestion), and cardiac muscles (which make your heart beat). Powerful stuff, right?
Lastly, we have the nervous tissue—the body’s electrical wiring. This is what allows you to feel pain, joy, hunger or even excitement when you get good news. It is made up of special cells called neurons that carry messages quickly between your brain, spinal cord, and the rest of your body. For example, when you touch something hot, it’s your nervous tissue that helps you pull your hand back in a flash!
Summary
- Epithelial tissue covers and protects body surfaces.
- Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues.
- Muscular tissue helps the body move.
- Nervous tissue carries messages around the body.
Evaluation
- Mention two places where epithelial tissue can be found.
- Explain in your own words why blood is considered a connective tissue.
- Which type of muscle tissue is responsible for heartbeats?
- What is the main function of nervous tissue?
I’m super proud of how far you’ve come. Remember, learning is like building a strong house—you lay one block at a time. Keep showing up, keep learning, and you’ll become a master in no time! Don’t forget, Afrilearn is always here to help you shine brighter. Can’t wait to learn with you again in the next lesson!
