Back to: ZOOLOGY 300 Level
Welcome To Class!
My dear friend, it’s great to see you again! Just think about how you dress differently depending on where you are — agbada in the north to protect from the sun, light clothes in Lagos heat, maybe raincoats in Calabar’s rainy season. That’s what adaptation is all about — changing to fit your environment. Today, let’s look at how reptiles and other animals adapt to where they live so they can survive, grow, and reproduce successfully.
Ecological Adaptations
What Are Ecological Adaptations?
Ecological adaptations are special features or behaviours animals develop to help them survive in specific environments. These could be physical (like body colour), physiological (like conserving water), or behavioural (like basking in the sun).
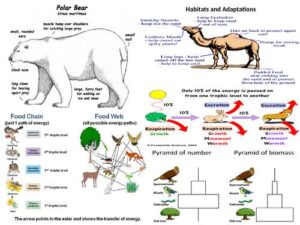
Adaptation is nature’s way of saying, “adjust or perish.” Every animal that survives in the wild has some kind of clever trick to deal with its surroundings. Whether it’s the desert, forest, swamp, or savannah — animals have their survival game on point.
Types of Ecological Adaptations in Reptiles
Reptiles are champions of adaptation, especially because they often live in tough environments. Let’s look at some of the ways they adjust:
- Structural adaptations
These are physical features that help them survive. For example, the rough, scaly skin of a lizard reduces water loss in dry areas like Katsina. The flat shell of a turtle helps it swim better, while the long body of a snake allows it to move through grass or sand easily. - Behavioural adaptations
These are habits animals form to stay alive. A snake might hide under rocks during the hot afternoon and come out at night when it’s cooler — just like how some farmers in the north work early in the morning and rest during midday heat. - Physiological adaptations
These involve internal body processes. Desert reptiles conserve water by producing very little urine, and some can even absorb moisture from food. This is just like how nomadic people in dry areas drink less water but still function efficiently.
Examples of Reptile Adaptations in Nigerian Environments
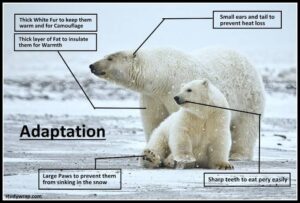
- Savannah: Reptiles like monitor lizards have tough skin to reduce water loss and dig burrows to escape the sun.
- Rainforest: Tree-dwelling reptiles like some geckos have sticky toe pads to climb trees and blend with leaves for camouflage.
- Wetlands: Crocodiles have eyes and nostrils positioned on top of their heads to see and breathe while mostly underwater — a great ambush tactic.
Each environment in Nigeria, from the hot north to the humid south, demands different strategies, and reptiles meet the challenge with amazing efficiency.
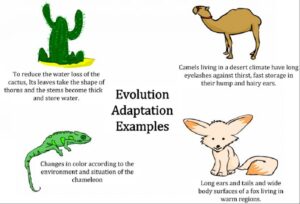
Summary
- Ecological adaptations are changes in structure, behaviour, or body function that help animals survive.
- Reptiles have adapted well to harsh environments through physical features, habits, and internal processes.
- Nigerian reptiles show different adaptations depending on whether they live in dry savannahs, rainforests, or wetlands.
Evaluation
- What are ecological adaptations, and why are they important?
- Explain the difference between structural, behavioural, and physiological adaptations.
- Describe one adaptation a reptile might have for surviving in a dry region of Nigeria.
- Give a real-life example of a reptile you’ve seen and how it behaves in its environment.
You’ve done excellently today! Remember, just like these animals adapt and survive, you too can learn, grow, and thrive no matter the challenges. Keep that learning fire burning, and know that Afrilearn is proud to be part of your success story. See you in the next exciting class!
