Back to: ZOOLOGY 300 Level
Welcome To Class!
Hi, my brilliant learner! It’s always a joy having you here. Get ready for a very interesting and touching lesson. Today, we’ll be talking about how animals give birth or lay eggs, how they feed their young, and how they care for them. You’ll see that even in the animal kingdom, being a parent is a serious responsibility!
Oviparity, Viviparity, Lactation, Parental Care
Oviparity (Egg-Laying)
Oviparity is when animals lay eggs that develop and hatch outside the mother’s body. This is the oldest method of reproduction and is still very common in many animals like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and some mammals (like the platypus).
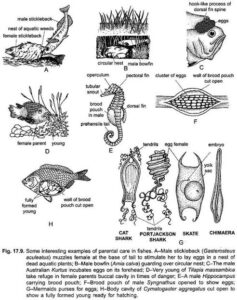
- The eggs usually have a protective covering—like jelly (in frogs) or hard shells (in birds).
- Most egg-laying animals lay many eggs at once because not all of them survive.
- Some provide no care after laying the eggs (like many fish), while others, like birds, sit on their eggs to keep them warm.
A good example is the hen. She lays eggs and sits on them to incubate until the chicks hatch. That’s oviparity in action!
Viviparity (Live Birth)
Viviparity is when animals give birth to live young instead of laying eggs. This method is common among most mammals, and also found in some reptiles and a few species of fish.
- The baby develops inside the mother’s womb.
- It receives nutrients directly from the mother through a placenta (in placental mammals).
- This method usually involves fewer offspring at a time, but with higher chances of survival.
Think about a goat or a dog. They carry their young in their womb and give birth to live babies that are then nursed and cared for.
Lactation
Lactation is the production of milk by the mammary glands in mammals. It is one of the most defining features of mammals.
- The mother feeds her babies with her milk, which is rich in nutrients and antibodies.
- It helps the young grow strong and healthy and builds their immunity.
- This is only seen in mammals—no other animal group produces milk this way.
Even humans are an example! Just like a lioness or a mother cow, human mothers breastfeed their babies to nourish and protect them in their early stages of life.
Parental Care
Parental care refers to all the ways parents protect, feed, and teach their young. It varies across species:

- Birds build nests, incubate eggs, and feed chicks.
- Mammals nurse their young, keep them warm, and teach them survival skills.
- Reptiles and amphibians generally offer little or no care, but there are exceptions—some snakes guard their eggs, and some frogs carry tadpoles on their backs.
Parental care increases the survival rate of young ones, especially when few are born at a time. Animals invest more time and energy in each child when they are fewer and more vulnerable.
Summary
- Oviparity is egg-laying, common in fish, birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
- Viviparity is giving birth to live young, mostly seen in mammals.
- Lactation is the feeding of young with milk by mammals, a unique trait of this group.
- Parental care helps the young survive and grow, and it varies greatly among animals—from no care to full care.
Evaluation
- What is the difference between oviparity and viviparity?
- Name two animals that are oviparous.
- Why is lactation important for mammals?
- Give one example of parental care in birds.
- Which animal group shows the most parental care, and why?
Wow! You’ve just learnt about some of the most beautiful and powerful things animals do—bringing life into the world and nurturing it. That’s a big deal! Keep shining bright, superstar. Afrilearn is always here to guide you with love and learning. See you next class!
