Back to: ZOOLOGY 500 Level
Welcome to class!
Good day, champion! I hope you’re feeling motivated and ready to add more skills to your Zoology toolkit. Today, we’re going to look at canopy cover and biomass estimation—two important ways ecologists measure the health and productivity of ecosystems. Whether you’re studying forests in Omo or savannahs in Jos, these tools will help you understand how much life and energy an area holds. Let’s break it down in a way that fits your world and studies perfectly.
Canopy Cover And Biomass Estimation
What is Canopy Cover?
Canopy cover is the layer of leaves and branches formed by trees and plants above the ground. Think about walking in a dense forest in Cross River—when you look up, the green leaves form a kind of roof that blocks sunlight. Measuring how much of the sky is covered by this “roof” helps ecologists know how much sunlight reaches the ground, which affects what animals and plants can live there.
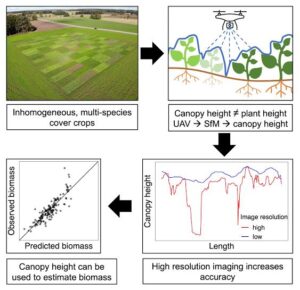
How to Measure Canopy Cover
One simple way is using a densiometer, a device with mirrors that lets you estimate the percentage of canopy overhead by counting reflections. If you don’t have one, you can take photographs facing up at different spots and later analyse how much of the picture is green leaves versus sky.
Imagine you are helping a community in Enugu study their forest to see if it’s healthy enough for animals like monkeys and birds. Measuring canopy cover tells you if there’s enough shade and shelter for these creatures.
What is Biomass Estimation?
Biomass is the total weight of all living plants and animals in a given area. Estimating biomass helps ecologists understand how much energy the ecosystem can support. In forests, biomass is often calculated by measuring the trees’ trunk size and using mathematical formulas to estimate their weight.
Methods of Biomass Estimation
In the field, you can measure tree diameter at breast height (DBH), usually about 1.3 metres above the ground. Using DBH and tree height, scientists apply standard equations to estimate the weight of the tree’s wood, leaves, and branches. Adding up all the trees gives an estimate of the total biomass.
For grasslands or farmlands, biomass can be estimated by clipping vegetation in a measured area, drying it, and weighing it.
Why Are These Measurements Important?
They help us know:
The health and productivity of forests and grasslands
How much carbon the ecosystem stores (important for fighting climate change)
The quality of habitat for wildlife
How land-use changes like farming or logging affect the environment
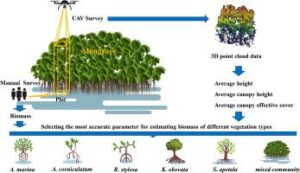
Real-Life Example
Chinwe, a final-year student at UNN, worked with a community near the Obudu Cattle Ranch. She measured the canopy cover in different forest patches to identify which areas were most suitable for bird nesting. She also estimated biomass to understand how much wood was available for sustainable harvesting without harming the ecosystem. Her work helped local people balance forest use and conservation.
Summary
- Canopy cover is the leafy “roof” formed by plants above the ground.
- Biomass estimation measures the total weight of living organisms in an area.
- Both are vital for assessing ecosystem health and sustainability.
- These measurements guide conservation and land management decisions.
Evaluation
- What does canopy cover tell us about an ecosystem?
- How is tree biomass estimated in the field?
- Why is biomass estimation important for understanding climate change?
- Suggest a simple way to estimate canopy cover if you don’t have special equipment.
You’re mastering important skills that make you a true steward of nature! With every lesson, your ability to understand and protect Nigeria’s amazing ecosystems grows stronger. Afrilearn is proud of your commitment—keep shining and keep learning. The world needs your knowledge and passion!
