Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 400 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hello, brilliant mind! It’s so wonderful to see you again. You’ve been learning some deep, exciting things, and today’s topic is right at the heart of modern science and innovation. We’re talking about Recombinant DNA Technology and Genetic Engineering. Don’t let the big words scare you—we’ll break it down simply, using clear, Nigerian-flavoured examples that will stick with you for life.
Recombinant Dna Technology And Genetic Engineering
What is Recombinant DNA Technology?
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology is a method scientists use to combine DNA from different organisms into one, in order to give an organism new traits.
Think of it like making a fruit salad—you take bananas, oranges, and pineapples from different places and mix them in one bowl. In rDNA, instead of fruits, scientists mix genes from different sources to make something new and useful.
For example, a gene from a bacteria that glows in the dark can be inserted into another organism, like yeast, so the yeast now glows. That’s recombinant DNA in action.
What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is the broader process of altering the genetic material (DNA) of an organism, and recombinant DNA is one of its major tools.
Through genetic engineering, scientists can improve organisms—make crops resist pests, bacteria produce insulin, or yeast create more alcohol. It allows us to design life in ways that solve real problems.
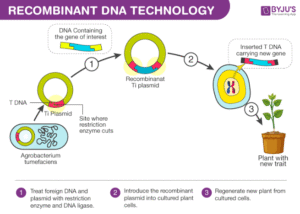
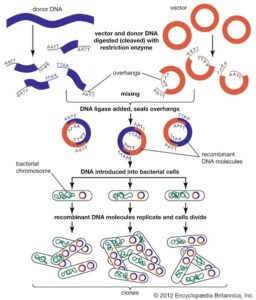
Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology
Isolation of DNA: The gene of interest (e.g., insulin gene) is taken from a source organism.
Cutting DNA: Special enzymes (restriction enzymes) cut the DNA at specific points.
Inserting into a Vector: The cut gene is inserted into a carrier (often a plasmid—a small circular DNA found in bacteria).
Transfer into Host: The recombinant plasmid is placed inside a host cell like E. coli.
Cloning and Expression: The host replicates and expresses the new gene—now it can produce the desired product (like insulin).
Let’s say you want to grow tomatoes that don’t spoil quickly. Scientists can take a gene from a microbe that produces a natural preservative and insert it into the tomato plant. Now the tomato lasts longer—this is genetic engineering at work.
A real-world Nigerian example is in medicine: many insulin medications used by diabetics today are made by genetically engineered bacteria that carry the human insulin gene.
Importance of rDNA and Genetic Engineering
Medicine: Production of insulin, vaccines, growth hormones.
Agriculture: Pest-resistant and drought-tolerant crops.
Industry: Microbes engineered to produce enzymes, ethanol, and other valuable chemicals.
Environmental Clean-up: Bacteria modified to digest oil spills or plastic.
Summary
- Recombinant DNA technology combines DNA from different organisms to create new traits.
- Genetic engineering is the broader science of changing DNA to improve organisms.
- rDNA involves cutting, inserting, and expressing desired genes in host organisms.
- These technologies help produce medicine, improve agriculture, and protect the environment.
- They are essential tools in modern microbiology and biotechnology.
Evaluation
- What is recombinant DNA technology?
- Mention three applications of genetic engineering.
- List the main steps in the recombinant DNA process.
This is advanced science, and you’re grasping it step by step—what a champion! Remember, every big innovation starts with a learner like you. Keep up the fantastic work, and let Afrilearn continue to support you as you grow into a world-class scientist. See you in the next class!
