Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 400 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
My dear friend, welcome back! It’s always a joy to see your commitment to learning. You’re doing something powerful—equipping yourself with knowledge that not only builds your future but also helps protect the health of millions. Today, we’re diving into a topic that forms the backbone of clean and safe food and drug production: Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Let’s walk through it together in a relatable, Nigerian way.
Good Manufacturing Practices (Gmp)
What Are Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)?
GMP refers to a set of rules, procedures, and practices that food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic manufacturers must follow to ensure products are safe, clean, high-quality, and consistently produced. These practices prevent contamination, errors, and fraud throughout the production process.

Think of GMP as a “code of conduct” for factories. Just like we wash our hands before cooking, manufacturers must follow strict cleanliness and process rules before producing food or medicine.
Why GMP Matters
Protects public health – GMP prevents dangerous products from reaching consumers.
Ensures quality – Each product meets the same high standard every time.
Promotes trust – Consumers are more confident in brands that follow GMP.
Fulfils legal requirements – Regulatory bodies like NAFDAC and SON enforce GMP rules in Nigeria.
Reduces waste – Proper processes reduce spoilage, defects, and costly recalls.
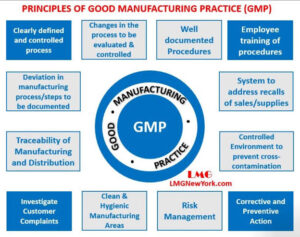
Key Principles of GMP

Personal Hygiene
Workers must maintain high levels of cleanliness—wearing gloves, uniforms, and hairnets.
Example: In a sachet water factory in Port Harcourt, staff must wash their hands and wear protective clothing before entering the production area.
Clean Facilities and Equipment
Machines, tools, and workspaces must be cleaned regularly and kept in good working condition.
Example: A yoghurt machine must be sterilised before use to prevent Listeria contamination.
Proper Documentation
Every step of production must be recorded—ingredients used, batch numbers, dates, etc.
This ensures traceability if something goes wrong.
Quality Raw Materials
Only approved and safe materials should be used. Spoiled or fake ingredients must be rejected.
Example: Using only NAFDAC-approved milk powder for ice cream.
Regular Training of Staff
Workers must be trained on hygiene, safety, and standard procedures.
Knowledgeable staff make fewer mistakes and produce safer products.
Pest Control
Factories must be free from insects, rodents, and birds.
Example: A bakery in Abuja uses sealed doors and traps to keep out pests.
Local Application in Nigeria
NAFDAC and SON inspect factories across Nigeria to ensure GMP is followed. If a company fails to comply, it may be shut down or fined. Companies that take GMP seriously build stronger reputations and reach both local and international markets.
Summary
- GMP is a system of practices that ensure the safe and consistent production of quality products.
- It protects public health, builds trust, and ensures compliance with legal standards.
- Key areas include hygiene, clean equipment, record-keeping, quality raw materials, and staff training.
- GMP is enforced in Nigeria by NAFDAC and SON.
- Factories following GMP reduce risks, save costs, and produce safer goods.
Evaluation
- What does GMP stand for, and why is it important?
- Mention three principles of GMP.
- Which two Nigerian agencies are responsible for enforcing GMP?
- Why must food factory workers wear protective clothing?
With every topic, you’re building skills that can change lives and shape industries. Stay consistent, stay focused, and know that Afrilearn is here to guide you all the way to excellence. Let’s keep moving forward together!
