Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 500 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
My ever-dedicated scholar, it’s always a joy having you here! You’ve already mastered the basics of PCR, so today we’re levelling up with something even more exciting—Real-Time PCR, also known as qPCR. If PCR is like a photocopy machine, real-time PCR is like a smart machine that tells you how many copies it’s making while it’s working. Let’s walk through this powerful tool together in a simple and relatable way.
Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
Let’s start with a quick refresher: in normal PCR, you make many copies of a specific DNA segment. But you don’t really know how much DNA you’ve made until the end, when you check with a gel. That’s a bit like cooking rice in a covered pot—you can’t tell if it’s ready until you open it.
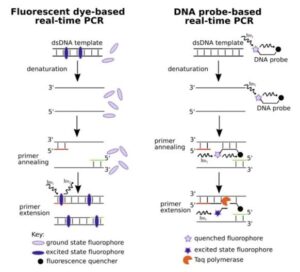
But real-time PCR (qPCR) is different. It allows scientists to monitor the DNA amplification process as it happens, cycle by cycle. That’s like using a transparent pot—you can see your rice cook in real time!
How Does Real-Time PCR Work?
qPCR uses fluorescent dyes or probes that glow when DNA is copied. As the DNA amount increases during the PCR cycles, the fluorescence also increases. The machine measures this light and displays it as a graph.
So, instead of waiting till the end, you get updates every few seconds—like seeing your Instagram likes go up in real time!
There are two common ways qPCR detects DNA:
SYBR Green Dye – This dye binds to double-stranded DNA and glows when the DNA is formed.
TaqMan Probes – These are more specific. They glow only when the target DNA is copied, reducing errors.
Why Is It Called “Quantitative” PCR?
Because qPCR doesn’t just tell you if a DNA sequence is present—it tells you how much is there. This is useful in:
Measuring virus load in patients (e.g., HIV, COVID-19)
Gene expression studies
Cancer diagnostics
GMO detection in crops
Real-life Nigerian example: Think of a fuel gauge in a car. It doesn’t just say “you have fuel”; it tells you how much—half tank, quarter tank, or full. That’s what qPCR does with DNA.
Key Terms to Know
Ct Value (Cycle threshold): This is the PCR cycle number where the fluorescence crosses a set threshold. The lower the Ct, the more DNA was present at the start.
Fluorescence curve: A graph that shows how DNA is increasing during the PCR cycles.
Summary
- Real-time PCR (qPCR) is a method that monitors DNA amplification as it happens.
- It uses fluorescent dyes or probes to measure DNA levels in real time.
- It provides both detection and quantification of DNA.
- qPCR is used in diagnostics, research, and genetic studies.
Evaluation
- What makes qPCR different from traditional PCR?
- What is a Ct value and what does it indicate?
- Give one real-life application of qPCR in medicine or agriculture.
Fantastic work today, superstar! You’ve now stepped into a more advanced space in molecular biology. Real-time PCR is changing the world—from saving lives in hospitals to improving crop quality in our farms. And now, you understand how it works! Keep going strong—Afrilearn is here for you all the way. Can’t wait to see you in the next class!
