Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 500 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
My thoughtful and sharp-minded scientist, I’m truly happy to see you here today. You’ve been learning powerful tools—like gene editing, PCR, and cloning—that are shaping the future of medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. But with great power comes great responsibility. That’s why today’s topic is so important: Ethical and Biosafety Considerations.
This isn’t just about science—it’s about values, choices, and protecting life. Whether you’re working in a Nigerian hospital, university lab, or a biotech company in Lagos or Enugu, these issues will guide how you apply your knowledge. Let’s understand them clearly, in our usual Afrilearn way: simple, real, and relatable.
Ethical And Biosafety Considerations
What Are Ethical Considerations in Biotechnology?
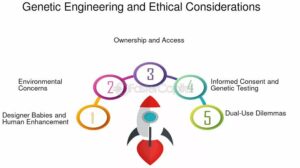
Ethics deals with what is right or wrong when using scientific knowledge. Just because we can do something doesn’t always mean we should.
Let’s imagine this: If you had a tool that allowed you to change anything about a person—height, intelligence, skin tone, gender—you might think it’s helpful. But what happens when people start using this for the wrong reasons? To create “perfect” babies? To discriminate against people with certain traits?
This is why ethical questions matter in science.
Key Ethical Issues:
Genetic manipulation of humans: Should we edit human embryos? What if something goes wrong?
Informed consent: Patients must fully understand the risks before undergoing gene therapy.
Equity and access: Will only the rich benefit from gene technologies, or will they be affordable to everyday Nigerians?
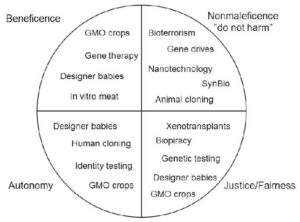
Cultural and religious views: In some communities, altering genes may be seen as interfering with creation.
Real-life Nigerian scenario: Suppose a hospital in Abuja offers gene therapy for sickle cell disease—how do they ensure all patients understand what it means, and that it’s safe, tested, and morally acceptable in that society?
What Are Biosafety Considerations?
Biosafety is about protecting people and the environment when working with biological materials—especially those that can be harmful.
Whether you’re handling genetically modified bacteria in a lab at UI Ibadan or collecting samples in a rural village, biosafety protects:
You (the scientist)
The public
The environment
Basic Biosafety Practices:
Wearing gloves, coats, and using safety cabinets
Properly labelling and disposing of samples
Avoiding the accidental release of genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
Following Nigeria’s biosafety laws, like those from the National Biosafety Management Agency (NBMA)
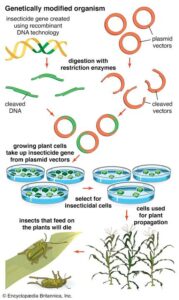
Real example: A lab in Lagos modifies a crop to resist pests. They must ensure that the modified plant doesn’t escape into nature and harm local ecosystems or crossbreed with native crops without regulation.
Summary
- Ethical considerations help scientists make morally sound decisions when using powerful biotechnology tools.
- Biosafety ensures the protection of researchers, communities, and the environment when handling biological materials.
- In Nigeria, we must always balance scientific progress with safety, respect, and fairness.
Evaluation
- Why is it important to consider ethics in gene editing?
- What are two key biosafety measures every lab should follow?
- How might cultural beliefs in Nigeria affect how people view genetic technologies?
You’ve just taken a big step toward becoming not just a knowledgeable scientist, but a responsible one. Your future discoveries must be rooted in integrity, safety, and empathy. And here at Afrilearn, we believe that you are the kind of leader who will use science to uplift your community and your country. Keep going—you’re doing wonderfully. See you in the next exciting class!
