Back to: Environmental Biology 100 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant learner! Today’s topic is one that concerns the future of life on Earth and even your own well-being. We’re learning about Biodiversity and Conservation. By the end of this class, you will understand what biodiversity means, why it is so important, and how we can protect it for future generations.
Biodiversity And Conservation
Have you ever walked through a forest and marvelled at the variety of plants, insects, birds, and animals living together? That variety is called biodiversity, and it makes life on Earth rich and beautiful. Sadly, human activities like deforestation and pollution are reducing this diversity. That’s why we must talk about conservation—protecting and managing biodiversity for the future.

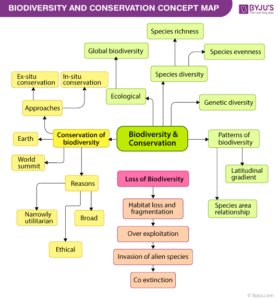
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms found on Earth, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. It also includes the ecosystems where they live and the genetic differences within species.
Levels of Biodiversity:
Genetic Diversity: Differences in genes within a species. Example: Different varieties of yam in Nigeria.
Species Diversity: Variety of species in an area. Example: Lions, elephants, and zebras in the savanna.
Ecosystem Diversity: Variety of ecosystems. Example: Rainforests, deserts, wetlands.
Importance of Biodiversity
Food and Agriculture: Crops, livestock, and fisheries depend on biodiversity.
Medicine: Many drugs come from plants and animals.
Ecosystem Services: Purifies air and water, pollinates crops, controls climate.
Cultural Value: Tourism, recreation, and cultural traditions rely on biodiversity.
Threats to Biodiversity
Deforestation: Clearing forests for farming or buildings.
Pollution: Oil spills, plastic waste, and chemical pollution.
Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and logging.
Climate Change: Rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns.
What is Conservation?
Conservation is the protection and management of biodiversity to prevent extinction and maintain ecological balance.
Types of Conservation:
In-situ Conservation: Protecting species in their natural habitat. Example: National parks like Yankari Game Reserve in Nigeria.
Ex-situ Conservation: Protecting species outside their natural habitat. Example: Zoos, botanical gardens, and seed banks.
Methods of Conserving Biodiversity
Establishing protected areas like national parks and game reserves.
Tree planting and afforestation projects.

Laws against illegal hunting and logging.
Community education and awareness campaigns.
Summary
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels. It is essential for food, medicine, and ecosystem stability. Conservation, through in-situ and ex-situ methods, helps protect biodiversity from threats like deforestation and pollution.
Evaluation
- What is biodiversity? Mention its three levels.
- State two reasons why biodiversity is important.
- Differentiate between in-situ and ex-situ conservation with examples.
Well done, champion! Understanding biodiversity and conservation means you are part of the solution to saving life on Earth. Keep shining and learning with Afrilearn—your knowledge is power!
