Back to: Environmental Biology 100 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant learner! Today, we’re taking a practical turn into something exciting—Fieldwork Preparation. Fieldwork is a vital part of Environmental Biology because it helps us study living things and their surroundings in their natural habitats. By the end of this lesson, you’ll know what fieldwork means, why it is important, and how to prepare for it properly.
Fieldwork Preparation
Imagine being in a lush forest, by a riverbank, or on open grassland, observing plants, animals, and their interactions. That’s fieldwork! It is an opportunity to step out of the classroom and experience nature first-hand. But before going out, proper preparation is key to making your field trip safe, productive, and fun.
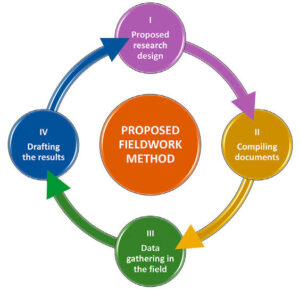
What is Fieldwork?
Fieldwork is the process of collecting data outside the classroom or laboratory, in the natural environment. It helps students and scientists gather real-life information about organisms, their behaviour, and their habitats.
Importance of Fieldwork
Provides hands-on experience with the environment.
Helps students understand ecological concepts better.
Encourages teamwork and observation skills.
Allows accurate collection of data for research and learning.
Steps in Fieldwork Preparation
Define the Objectives
Clearly state why you are going on the trip.
Example: To study different types of plants in a rainforest.
Choose the Study Area

Select a location suitable for your objectives.
Example: A riverbank for aquatic species or a forest for biodiversity studies.
Seek Permission and Inform Authorities
Get approval from school or local authorities before going to a protected area.
Plan the Logistics
Transportation: Arrange vehicles or buses.
Time: Fix a convenient date and time, usually during the day.
Prepare Materials and Equipment
Basic tools: Notebooks, pens, pencils.
Sampling tools: Nets, jars, quadrats, soil augers.
Protective gear: Boots, gloves, hats, sunscreen.
First Aid Kit: For treating minor injuries.
Safety Precautions
Wear appropriate clothing (long sleeves to prevent insect bites).
Avoid touching unknown plants or animals.
Stay with the group to avoid getting lost.
Carry water and light snacks.
Data Collection Methods in Fieldwork
Observation: Watching species and their behaviour.
Counting and Sampling: Using quadrats to estimate population size.
Recording: Taking notes and photographs for documentation.
Summary
Fieldwork involves collecting data from the natural environment to understand ecosystems better. Proper preparation includes setting objectives, selecting the site, arranging logistics, gathering tools, and observing safety measures.
Evaluation
- Define fieldwork and state its importance.
- List four items you should carry for fieldwork.
- Mention two safety measures during fieldwork.
Fantastic job! You are now ready to experience real-world biology with confidence and safety. Keep learning with Afrilearn—your curiosity will take you far!
