Back to: Environmental Biology 200 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant learner! Have you ever seen a farm full of maize, yams, or cassava and wondered how all the plants grow so well together? That farm is not just a collection of plants; it is an agroecosystem — a system where crops, animals, soil, water, and humans all work together. Today, we will learn about Agroecosystems and Soil Health, and by the end of this lesson, you will understand why healthy soil is the foundation of good farming and food production.
Agroecosystems And Soil Health
What is an Agroecosystem?
An agroecosystem is a type of ecosystem that is designed and managed by humans for food production. Examples include rice farms in Kebbi, cocoa plantations in Ondo, and tomato farms in Kano. Unlike natural ecosystems, agroecosystems rely on humans to provide inputs like fertilisers, irrigation, and pest control.
Components of an Agroecosystem
Crops and animals: Plants like yam, cassava, maize, and livestock like poultry or goats.
Soil: The base where plants grow and get nutrients.
Water: Essential for irrigation and plant growth.
Farmers: Humans who plan, plant, and manage the system.
Tools and technology: Tractors, irrigation systems, and organic fertilisers.
What is Soil Health?
Soil health refers to the soil’s ability to support plant growth, store nutrients, and sustain life. A healthy soil is rich in organic matter, has good texture, and is full of living organisms like earthworms and microbes. Healthy soil produces better crops and protects the environment.
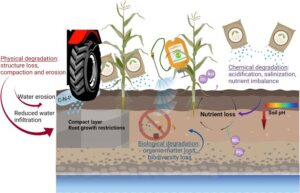
Factors that Affect Soil Health
Erosion: Wind and water wash away the topsoil, which is the most fertile part.
Overuse of chemicals: Too many pesticides or fertilisers can kill good microbes in the soil.
Deforestation: Clearing trees exposes the soil to erosion.
Overgrazing: Too many animals feeding on the land damage vegetation and soil structure.
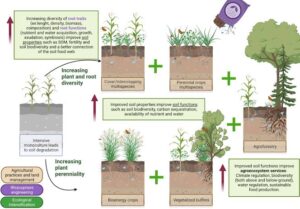
Maintaining Soil Health
Farmers can keep soil healthy by:
Crop rotation: Planting different crops each season to improve soil nutrients.
Adding organic matter: Using compost, animal manure, or crop residues.
Planting cover crops: Grasses or legumes that protect the soil during off-seasons.
Contour farming and terracing: Reducing erosion on sloped lands.
Importance of Healthy Agroecosystems
They produce safe and abundant food.
They reduce the need for harmful chemicals.
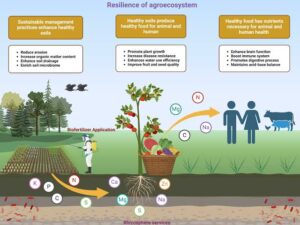
They help conserve water and nutrients.
They support biodiversity by attracting pollinators like bees.
Summary
- An agroecosystem is a managed ecosystem for food production.
- Soil health is the ability of soil to support plant growth and life.
- Erosion, chemicals, and overgrazing harm soil health.
- Crop rotation, composting, and cover crops improve soil quality.
Evaluation
- What is an agroecosystem?
- Mention three components of an agroecosystem.
- List two ways farmers can maintain soil health.
- Why is soil health important for food security?
You did a wonderful job today! Always remember, healthy soil means healthy food and healthy people. Keep learning with Afrilearn — you’re growing your knowledge just like a well-tended farm.
