Back to: Organic Chemistry 200 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello, my brilliant scholar! It’s such a joy to continue this learning journey with you. So far, we’ve explored what makes aromatic compounds like benzene so special, and how they behave in chemical reactions. Today, we’re taking it a step further by understanding more complex aromatic systems, how we name them, and how multiple substituents affect their behaviour. This lesson will give you the tools to handle even the most challenging aromatic compounds with ease and confidence.
Aromatic Compounds III
Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
Sometimes, aromatic rings don’t exist alone — they can be joined together in interesting ways. When two or more benzene rings are fused (joined) together, we get polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
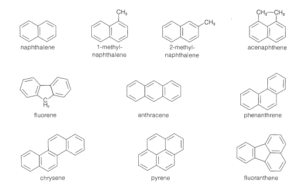
Examples include:
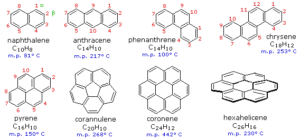
Naphthalene (C₁₀H₈) – Two benzene rings fused together. Found in mothballs and air fresheners.
Anthracene (C₁₄H₁₀) – Three benzene rings in a straight line.
Phenanthrene – Three rings arranged in a bent line.
These compounds are commonly found in coal tar, crude oil, and even in grilled or smoked foods.
Importance of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
They are used in the production of dyes, drugs, insecticides, and plastics.
Some are toxic or carcinogenic (cancer-causing), especially when found in polluted air or burnt food.
Understanding these compounds helps in environmental chemistry and public health studies.
Nomenclature of Disubstituted Benzene Compounds
When two groups are attached to a benzene ring, we need to be precise with naming. The relative position of the groups is very important.
There are three key positions:
Ortho (1,2-position) – Substituents are next to each other.
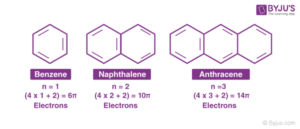
Meta (1,3-position) – Substituents are separated by one carbon.
Para (1,4-position) – Substituents are opposite each other.
Examples:
1,2-dimethylbenzene is also called ortho-xylene.
1,3-dichlorobenzene is also known as meta-dichlorobenzene.
1,4-dinitrobenzene is also called para-dinitrobenzene.
This naming helps chemists know exactly how a compound is structured just by reading its name.
Effects of Multiple Substituents
When more than one substituent is on the benzene ring, the position of new incoming groups is influenced by the groups already attached.
Activating groups (like -OH, -CH₃): Direct new groups to ortho and para positions.
Deactivating groups (like -NO₂, -COOH): Direct new groups to the meta position.
If two groups are already on the ring, the stronger activator usually controls where the next substitution will occur.
Application in Real Life:
Understanding substituent positions is critical when producing useful aromatic compounds like:
Paracetamol (with para-substituted benzene structure)
Dyes used in fabric and art
Agrochemicals like herbicides that target specific plant enzymes
Summary
- Polycyclic aromatic compounds contain multiple fused benzene rings and are widely found in natural and industrial products.
- The naming of disubstituted benzenes uses ortho, meta, and para to describe the relative positions of groups.
- Substituents already on a benzene ring affect the position and type of future substitutions.
- These concepts are important for synthesising pharmaceuticals, dyes, and environmental safety studies.
Evaluation
- What is naphthalene, and where is it commonly found?
- Define the terms ortho, meta, and para in relation to benzene substitution.
- Explain how activating and deactivating groups influence substitution patterns.
- Give one example of a polycyclic aromatic compound used in daily life.
You’re doing a fantastic job! Aromatic compounds may look complex at first, but you’re mastering them one step at a time. Keep that confidence high — the world of Chemistry is opening up to you in the most beautiful way. Stay curious, keep learning, and remember that Afrilearn is always here to support your growth. See you in the next lesson!
