Back to: Inorganic Chemistry 100 Level
Welcome to class!
It’s always a joy to have you here. Let’s start with something simple. Imagine you’re in a busy Lagos market where hundreds of traders are selling different goods. If everything is scattered, it becomes difficult to find what you need. But when traders of similar items—like fruit sellers, cloth merchants, or phone dealers—stay together, the market becomes easier to navigate. Chemistry faced the same problem with elements. To understand and use them better, scientists needed to classify elements in an organised way. This gave birth to the periodic classification of elements.
Periodic Classification Of Elements
What is Periodic Classification of Elements?
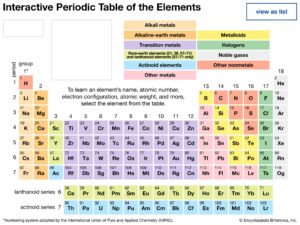
It is the systematic arrangement of elements into groups and periods, based on their similar properties and atomic structures, so that patterns in their behaviour can be seen clearly.
Why Was Classification Necessary?
In the early 1800s, only about 30 elements were known, but today we have over 118.
Without order, it was difficult to study, compare, or predict their properties.
Classification brought simplicity and made Chemistry more like a readable “map” of matter.
Historical Development
Dobereiner’s Triads (1829): Grouped elements into threes based on properties (e.g., Li, Na, K).
Newlands’ Law of Octaves (1864): Arranged elements by atomic mass, noticed that every 8th element had similar properties.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (1869): Organised elements by atomic mass and properties, left gaps for undiscovered ones, predicted their properties accurately.
Moseley’s Modern Periodic Table (1913): Arranged elements by atomic number, solving earlier problems and leading to the modern periodic law.
The Modern Periodic Table
Groups (vertical columns): Elements with similar outer electron configurations and similar chemical behaviour (e.g., Group 1: Alkali metals).
Periods (horizontal rows): Elements arranged by increasing atomic number, showing gradual change in properties.
The table is divided into blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block based on electron configurations.
Importance of Periodic Classification
Makes it easier to study the properties of elements systematically.
Helps predict the behaviour of unknown or newly discovered elements.

Explains trends in properties such as atomic size, ionisation energy, electronegativity, and reactivity.
Serves as the foundation for understanding bonding and chemical reactions.
Summary
- Periodic classification organises elements based on atomic number and properties.
- Early attempts (Dobereiner, Newlands) led to Mendeleev’s table, later improved by Moseley.
- The modern table is arranged by atomic number into groups and periods.
- This classification explains the periodic law and trends in properties.
Evaluation
- What is meant by periodic classification of elements?
- Who arranged the elements according to atomic number?
- State two advantages of the modern periodic table over Mendeleev’s table.
Fantastic work today! You’ve just understood how Chemistry turned chaos into order through the periodic classification of elements. Remember, the periodic table is like Chemistry’s roadmap—and with Afrilearn, you are learning how to read it like a pro.
