Back to: LITERATURE IN ENGLISH SS1
Welcome to class!
We are thrilled to have you in our class!!
In today’s class, we will be talking more about the genres of literature. Enjoy the class!
Genres of Literature II
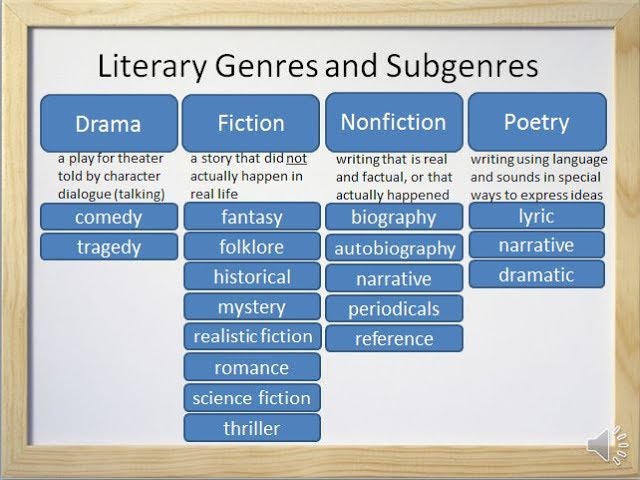
Preamble
Recall that in the previous week, it was established that there are three genres of literature namely: Poetry, Drama and Prose. Also, attempts were made to examine the genre known as poetry, its characteristics as well as its types. In this lesson, the literary genre known as drama will be examined just as it was done for poetry.
Drama:
This literary genre is often also referred to as a play and is performed in front of an audience. It is a literary work meant to be performed on stage by casts/actors or actresses. Dramas are written through dialogue and include stage directions for the actors to follow. The characteristics of drama are: It is written in acts and scenes; it is acted or performed on stage by actors and actresses; It has a prologue and an epilogue; The dialogue between characters is made up of sentences; It makes use of dialogue among characters to convey its message to the audience; It makes use of costumes and props.
The Importance of Being Earnest by Oscar Wilde would be considered a drama because it is written through dialogue in the form of a script that includes stage directions to aid the actors in the performance of the play.
Types of drama
In literature, there are three forms/kinds of drama and they include the following:
- Comedy
- Tragedy and
- Tragi-comedy
Comedy:
This is a type of drama which is characterized by its humorous or satirical tone and depicts amusing people or incidents, in which the characters ultimately triumph over adversity. There are various types of comedy such as parody, satire, comedy of manners, romantic comedy, farce, burlesque, among others. An example of a comedy is Oliver Goldsmith’s She Stoops to Conquer.
Tragedy:
This is a type of drama that treats a serious subject about human suffering or a terrible event in a dignified style in the life of a hero, whose “tragic flaw or hamartia” leads to his/her downfall and has an unhappy ending. It also invokes “pleasure or catharsis” in its audience. An example of this is William Shakespeare’s tragedies such as Hamlet, Othello, Macbeth, Julius Caesar, King Lear and so on.
Tragi-comedy:
This type of drama combines the elements of or is a mixture of both the type of drama known as the comedy and tragedy. It is also seen to be described as either a tragic play which contains enough comic elements to lighten the overall mood or a serious play with a happy ending. An example of this is William Shakespeare’s The Merchant of Venice.
Nevertheless, the literary genre known as prose is examined below in-depth. This is done to achieve an understanding of the phenomenon in question.
Prose
The prose is a form of language that has no formal metrical structure. It applies a natural flow of speech, and ordinary grammatical structure, rather than rhythmic structure, such as in the case of traditional poetry. Normal everyday speech is spoken in prose, and most people think and write in prose form. In addition, the prose is a type of writing that is written through the use of sentences. These sentences are combined to form paragraphs. This type of writing is broad.
In another view, the prose is the use of natural language and speech within a closely defined structure of writing. It is different from poetry in that it is not rhythmically structured. It is used with many different forms of literature, history and philosophy. There are two main types of prose namely: Fiction and Non-fiction. To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is an example of fictional prose. It is written in complete sentences and divided through paragraphs. Some of the characteristics of prose are
- it is written in chapters and paragraphs
- it is made up of characters
- it has a plot
- it is written in complete sentences, and so on
Fiction
This is the form of any work that deals, in part or whole, with information or events that are not real, but rather, imaginary and theoretical, that is, invented by the author. Moreover, fiction is a type of prose that is not real. Authors have the freedom to create a story based on characters or events that are products of their imaginations. While fiction can be based on true events, the stories they tell are imaginative in nature.
Like poetry, this genre also uses figurative language; however, it is more structural in nature and more closely follows grammatical conventions. Fiction often follows Freytag’s plot pyramid that includes an exposition, inciting incident, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, and dénouement. The novel Slaughterhouse-Five by Kurt Vonnegut is an example of a fictional story about the main character’s experience with his self-acclaimed ability to time travel.
Types of fiction
There are various types of fiction in literature and they include:
- Mystery
- fantasy
- fable
- allegory
- parables
- romance
- folktales and
- creative writing
Mystery:
This is something that us impossible or difficult to figure out. It can be a secret, riddle or a puzzle, hence needs intelligence in order to reveal the unknown. A mystery is mostly an investigation activity whereby a detective has to solve a puzzle so as to find a solution to crime and crack the case.
Fantasy:
This is a type of fiction that employs magic and other supernatural phenomena as primary plot element theme or setting. Many works within the genre take place in imaginary worlds where magic and magical creatures are common. It is distinguished from the genres of science fiction and horror by the expectation that it steers clear of scientific and macabre themes, respectively, though there is a great deal of overlap between the three, all of which are sub-genres of speculative fiction.
Fable:
This is a succinct fictional story in prose or verse, that features animals, mythical creatures, plants, inanimate o objects or forces of nature which are anthropomorphized(I.e. given human qualities such as verbal communication), and that illustrated or leads to an interpretation of a moral lesson, which may at the end be added explicitly in a pithy maxim.
Allegory:
This is a rhetorical device in which characters or events in a literary, visual, or musical art form represent or symbolize ideas and concepts. Allegory has been used widely throughout the histories of all forms of art; a major reason for this is its immense power to illustrate complex ideas and concepts in ways that are easily digestible and tangible to its viewers, readers, or listeners. An allegory conveys its hidden message through symbolic figures, actions, imagery, and/or events. Allegory is generally treated as a figure of rhetoric; a rhetorical allegory is a demonstrative form of representation conveying meaning other than the words that are spoken.
Parables:
This is a succinct didactic story, in prose or verse, which illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects or forms of nature as characters, whereas parables have human characters. A parable is a type of analogy.
Romance:
This is the expressive and pleasurable feeling from an emotional attraction towards another person associated with love. In the context of romantic love relationships, romance usually implies an expression of one’s strong romantic love or one’s deep and strong emotional desires to connect with another person intimately or romantically.
Folktales:
A folktale is a story or legend handed down from generation to generation usually by oral retelling. Folktales often explain something that happens in nature or convey a certain truth about life. They are in truth about life. They are fictitious stories told to amuse and amaze the listeners.
Creative Writing:
This is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, allegoric or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics. It can be technically considered to be any writing of original composition. In this sense, creative writing is more contemporary and process-oriented name for what has been traditionally called literature, including the variety of its genres.
Non-fiction
Non-fiction is another type of prose that is factual rather than imaginative in nature. Because it is more factual and less imaginative, it may use less figurative language. Nonfiction varies however from piece to piece. It may tell a story through a memoir or it could be strictly factual in nature like a history textbook.
Moreover, non-fiction is one of the two main divisions in prose writing the other form being fiction. It is a story based on real facts and information. It is a narrative, account, or other communicative work whose assertions and descriptions are believed by the author to be factual. These assertions and descriptions may or may not be accurate, and can give either a true or false account of the subject in question; however, it is generally assumed that authors of such accounts believe them to be truthful at the time of their composition or at least, pose them to their audience as historically or empirically true. The memoir Night by Elie Wiesel is a memoir telling the story of Wiesel’s experience as a young Jewish boy during the Holocaust.
Types of non-fiction
There are several types of non-fiction in literature and they include:
- biography
- autobiography
- memoir
- diary or Journal
- essay
- historical document or speech
- documentary, and so on.
Biography:
This is a book about a person’s life written by someone else. It is also known as a bio. It is a detailed description or account of a person’s life. It entails more than basic facts like education, work, relationships, and death – a biography also portrays a subject’s experience of these events.
Autobiography:
This is a book that someone writes about his or her own life. It is a written account of the life of a person written by that person. It is based on the writer’s memory. It is closely associated with the memoir.
Memoir:
This is a book a person writes about a particular time in his or her lifetime. It does not cover from birth to death. It is a collection of memories that an individual writes about moments and events both public and private that took place in the author’s life. The memoir tells a story from a life, the whole autobiography tells the story of a life.
Diary or Journal:
This is a day by day account of a person’s life. It is a record with discrete entries arranged by date reporting on what has happened over the course of a day or other period. A personal diary may include a person’s experiences, and/or thoughts or feelings, including comment on current events outside the writer’s direct experience.
Essay:
This is a short non-fiction work about a particular topic called an essay. It looks at one subject in a limited way. Essays are generally short pieces of writing written from an author’s personal point of view, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of an article, a pamphlet and a short story.
Historical Document or Speech:
This is an official statement that records the social and political beliefs of groups of people, and individuals in history and exposes the readers to the language and attitude of the time.
Documentary:
It is a non-fiction form that uses primary and secondary sources.
In summary, by exploring the genres of literature, we develop a deeper understanding of the diversity and richness of literary works as they relate to the genres of literature.
Evaluation
What themes are explored in “The Time Machine” and “The Wizard of Oz”?
Reading Assignment
What are the different genres of literature discussed in this note?
Weekend Assignment
Discuss the importance of genres in literature and how they help readers understand and appreciate literary works.
We hope you enjoyed today’s class. In our next class, we will be talking about Prose.
Let us know your thoughts and questions in the comment section, and we will attend to them as fast as we can.
