Back to: ZOOLOGY 200 Level
WELCOME TO CLASS
Today, we’re going to explore another crucial aspect of animal anatomy—appendages and segmentation. These two features are essential for understanding how many animals move, interact with their environment, and perform various functions necessary for survival. Let’s take a look at how these elements contribute to the animal kingdom’s incredible diversity!
Appendages And Segmentation
Appendages: Structure and Function
Appendages are specialized body parts that extend from the body of an organism and serve a variety of functions, such as movement, feeding, and sensing. In arthropods, appendages include legs, antennae, mouthparts, and wings, all of which are adapted to the specific needs of the animal.
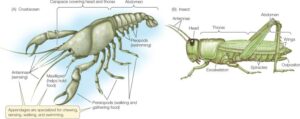
For example, in insects, the legs are used for walking, jumping, or swimming, while antennae act as sensory organs to detect chemical signals, temperature, and even vibrations in the air. The mouthparts vary greatly, depending on the type of food the animal eats. Some have chewing mouthparts, while others, like mosquitoes, have piercing or sucking mouthparts.
In marine arthropods like crabs, appendages like claws (chelae) are used for both capturing food and defending against predators. These appendages are important because they help animals interact with their environment in very specific ways, depending on their habitat and lifestyle.
Segmentation: The Building Blocks of Complexity
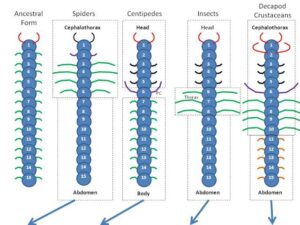
Segmentation refers to the division of the body into repeated sections or segments, each of which may have a similar structure but can be adapted for different functions. This feature is most commonly seen in arthropods and annelids (such as earthworms).
In arthropods, segmentation allows for a more specialized and flexible body plan. The body is divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen. Each segment may have different appendages, such as legs or wings, depending on its function. For example, in insects, the thoracic segments are dedicated to locomotion, with each segment carrying one pair of legs, while the abdominal segments are primarily concerned with digestion and reproduction.
In annelids, like earthworms, segmentation is also essential for movement. The repeated segments allow the animal to contract and extend its body in a coordinated manner, aiding in burrowing and locomotion.
Segmentation provides a degree of flexibility, allowing animals to develop specialized body parts and adapt to different environments. For example, it allows the insect to move more efficiently, while the segmented body of an earthworm helps it to wriggle through the soil.
Importance of Appendages and Segmentation
Both appendages and segmentation offer significant advantages for the survival of animals. Appendages allow for a wide range of movements and functions, from walking to feeding and mating. They enable animals to interact effectively with their environment, improving their chances of finding food, avoiding predators, and reproducing.
Segmentation enhances flexibility and the ability to specialize different body parts for different functions. This enables animals to become highly adapted to their environment, whether they are burrowing, flying, or swimming. The repeated segments allow for both movement and more efficient organ development.
Summary
- Appendages are specialized body parts that assist with movement, feeding, and sensing.
- Segmentation divides the body into repeated sections that can be specialized for different functions.
- The combination of appendages and segmentation allows animals to perform complex tasks and adapt to diverse environments.
- In arthropods, segmentation contributes to the flexibility of their body plan, while in annelids, it aids in movement.
Evaluation
- What are some examples of appendages in arthropods, and what functions do they serve?
- Explain the role of segmentation in arthropods and annelids.
- How do appendages and segmentation work together to help an animal survive in its environment?
- What is the importance of having specialized appendages, such as claws in crabs or antennae in insects?
Well done for grasping how appendages and segmentation play such vital roles in the survival and success of animals. Keep up the great progress, and get ready for our next exciting lesson. Keep the curiosity flowing, and let’s continue this journey together!
