Back to: Botany 100 Level
Hello, my brilliant Afrilearn scholar! I hope you’re having a fantastic day! Have you ever wondered what makes up a plant? Just like a house is built with bricks, plants are made up of tiny building blocks called cells. These plant cells have different parts, each with a special job, just like different rooms in a house. Today, we are going to learn about the basic structure of plant cells and how their parts help plants survive, grow, and make food.
Basic Structure Of Plant Cells: Cell Wall, Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm, Organelles (Nucleus, Chloroplasts, Mitochondria, Vacuoles)
Basic Structure of Plant Cells
A plant cell is a small unit of life that performs all the functions a plant needs to grow and stay alive. Plant cells have different parts, called organelles, which work together like a well-organised factory. Let’s look at the main parts of a plant cell and their functions.

1. Cell Wall – The Protective Shield
The cell wall is a thick, strong layer that surrounds the plant cell.
It is made of cellulose, which gives the plant its rigid shape and helps it stand upright.
The cell wall protects the cell and prevents it from bursting when it absorbs too much water.
Without the cell wall, plants would be soft and unable to grow tall!
2. Plasma Membrane – The Gatekeeper
Just inside the cell wall, the plasma membrane (cell membrane) controls what enters and leaves the cell.
It allows important substances like water, oxygen, and nutrients to pass through while keeping harmful substances out.
Think of it like a security guard at a gate, allowing only the right people to enter.
3. Cytoplasm – The Cell’s Workspace
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance inside the cell that holds all the organelles in place.
It contains water, enzymes, and nutrients that help the cell function properly.
This is where most of the cell’s activities take place, like a busy market where different things happen at the same time.
4. Organelles – The Specialised Workers in the Cell
Plant cells contain several organelles, each with a specific job. Let’s take a look at them:
a. Nucleus – The Control Centre
The nucleus is the brain of the cell, controlling all activities inside the cell.
It contains DNA, which carries the instructions for how the plant grows, develops, and reproduces.
Think of the nucleus as the headmaster of a school, making sure everything runs smoothly.
b. Chloroplasts – The Food Factory
Chloroplasts are green structures found in plant cells.
They contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that helps plants absorb sunlight for photosynthesis (the process of making food).
Without chloroplasts, plants would not be able to make their own food, and life on Earth would not exist!
c. Mitochondria – The Powerhouse
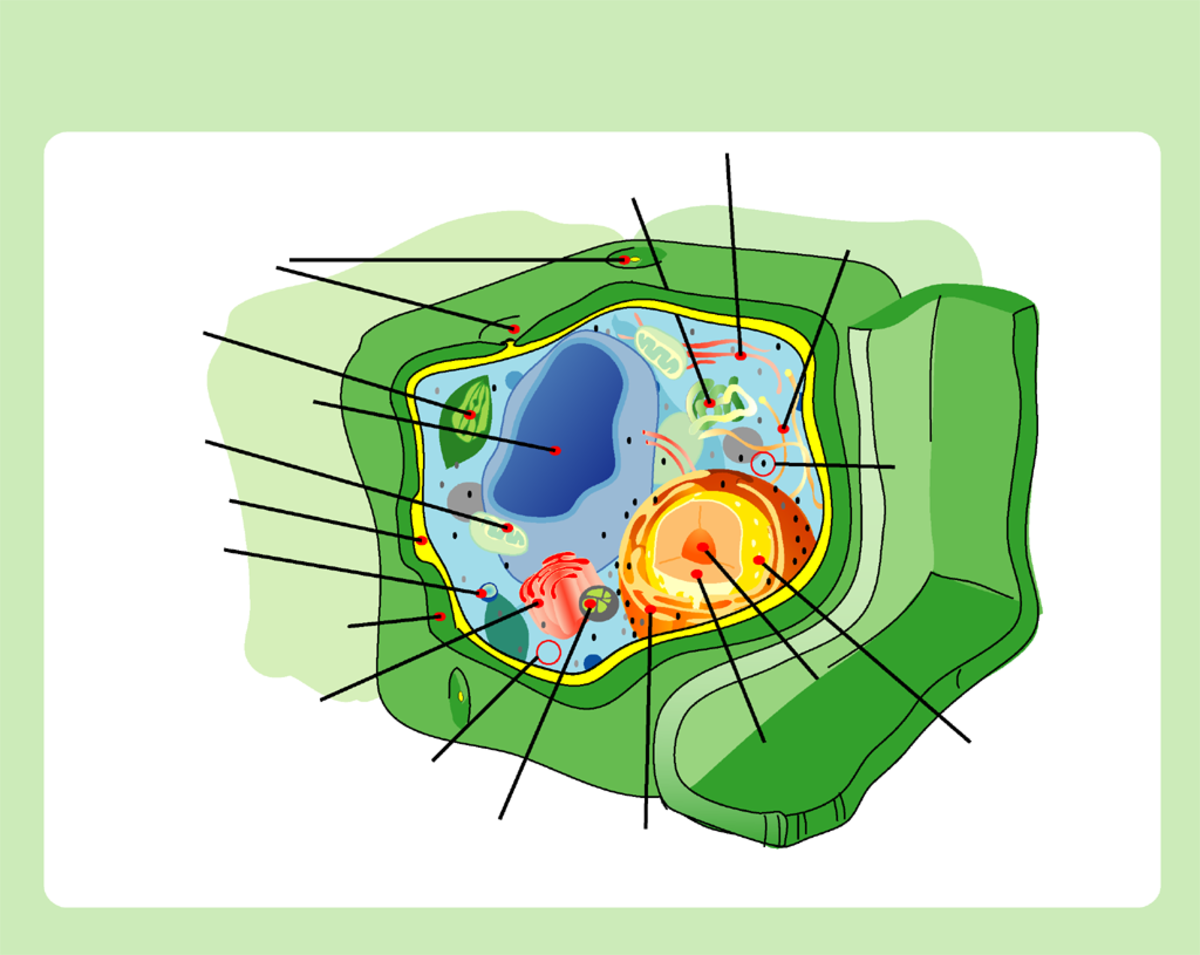
The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell.
They break down food and release energy that the plant uses for growth and other activities.
Just like generators provide electricity to a house, mitochondria provide energy to the cell.
d. Vacuoles – The Storage Tank
The vacuole is a large sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products.
In plant cells, the vacuole is very large and helps maintain the cell’s shape.
When a plant does not get enough water, the vacuole shrinks, and the plant wilts. But when it absorbs water, the vacuole swells, making the plant stand tall and fresh.
Summary
Plant cells are made up of different parts, each with a unique function.
The cell wall gives the plant its shape and support.
The plasma membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell.
The cytoplasm holds all the cell parts and allows important activities to take place.
The nucleus controls the cell’s activities, like a command centre.
Chloroplasts help the plant make food through photosynthesis.
Mitochondria provide energy for the cell’s activities.
The vacuole stores water and nutrients and helps the plant stay firm.
Evaluation
- What is the function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
- Why is the plasma membrane important to the plant cell?
- What is the role of chloroplasts in a plant cell?
- How do mitochondria help the plant cell function?
- Why is the vacuole larger in plant cells compared to animal cells?
You are doing amazing! Plant cells may be tiny, but they are full of life and energy—just like you! Keep learning, stay curious, and always believe in your ability to grow. See you in the next lesson!
