Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 100 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
It’s great to have you back again! Today, we’re going to learn about something that connects science with farming and food — Biofertilizers and Enzymes. These are important tools that show how useful microorganisms can be in improving soil health, growing food, and even making medicines. By the end of this class, you’ll understand how these biological helpers support life in amazing ways.
Biofertilizers And Enzymes
Biofertilizers
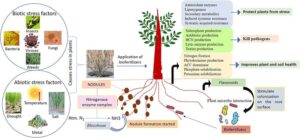
Biofertilizers are living microorganisms added to the soil to help increase the availability of nutrients to plants. They are natural and eco-friendly alternatives to chemical fertilisers. In a country like Nigeria where many farmers are turning to more sustainable farming methods, biofertilisers are becoming more and more important.
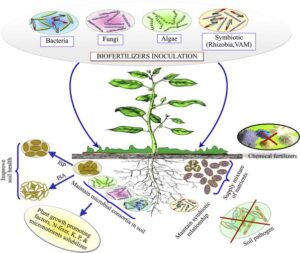
They work by:
Fixing nitrogen from the air into a form plants can use.
Solubilising phosphorus, making it available to plant roots.
Improving soil structure and promoting plant growth naturally.
Common examples include:
Rhizobium – lives in the root nodules of legumes (like beans, groundnuts) and fixes nitrogen.
Azospirillum – helps cereals like maize and millet grow better.
Azotobacter – lives freely in the soil and fixes nitrogen.
Mycorrhiza – fungi that increase water and nutrient absorption for plants.
Example: A farmer in Jos grows groundnuts. Instead of only using chemical fertilisers, she uses Rhizobium-based biofertiliser. Her crop grows healthier, and the soil stays fertile for the next season — a win-win!
Enzymes
Enzymes are biological catalysts — they are proteins produced by living organisms (including microbes) that speed up chemical reactions without being used up.
In microbiology and biotechnology, microbial enzymes are used in many industries, such as:
Food industry – Amylase breaks down starch into sugar during bread and beer production.
Dairy – Rennin or chymosin helps curdle milk to make cheese.
Medical use – Streptokinase is used to dissolve blood clots.
Detergent industry – Protease helps break down protein stains in laundry.
Textile industry – Enzymes are used to soften fabrics and improve colours.
Example: In a factory in Ibadan, enzymes are added to laundry detergents to make clothes cleaner, especially for removing food or sweat stains — that’s the work of protease.
Why This Topic Matters
Biofertilisers and enzymes show how nature provides sustainable solutions. Instead of relying heavily on chemicals that can harm the environment, microbes help us grow food, make medicines, and process products in cleaner and safer ways.
Summary
- Biofertilizers are live microbes that improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen and solubilising nutrients.
- Examples of biofertilizers include Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Mycorrhiza.
- Biofertilizers promote eco-friendly farming and maintain healthy soil.
- Enzymes are proteins produced by microbes that speed up chemical reactions.
- Enzymes are used in food production, medicine, detergents, and more.
Evaluation
- What are biofertilizers, and how do they help farmers?
- Give two examples of microorganisms used as biofertilizers.
- Define enzymes and list two industries where microbial enzymes are used.
- Why are biofertilizers better than chemical fertilisers for long-term use?
It’s exciting to see how microbes are used not just in labs, but in real-life farming, food, and factories. You are gaining the knowledge to help build a healthier, greener future for Nigeria and beyond. Keep shining — Afrilearn is proud to be part of your journey. See you in the next class!
