Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 100 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant mind! I’m so happy to have you back today. You’re doing an excellent job, and every step you take brings you closer to becoming a great microbiologist. Today’s lesson is about the different branches of microbiology and how they apply to real life—especially here in Africa, from our farms to our hospitals, kitchens, and even rivers. Let’s get right into it!
Branches And Applications Of Microbiology
Branches of Microbiology
Microbiology isn’t just one subject—it’s like a big tree with many branches, and each branch focuses on a particular type of microorganism or activity. Let’s look at some important ones:
1. Bacteriology
This is the study of bacteria. Some bacteria help us, like those used in yoghurt and fermented locust beans (iru), while others cause diseases like typhoid and tuberculosis.
2. Virology
This branch deals with viruses. From the common cold to HIV and COVID-19, virologists work hard to understand how viruses behave, spread, and how to stop them.
3. Mycology
Mycology is the study of fungi. Some fungi are useful—like the ones that help in baking bread—while others cause infections like athlete’s foot or spoilage of food during the rainy season.
4. Parasitology
This is the study of parasites—organisms that live in or on other living things. In Nigeria, we’re very familiar with diseases like malaria and schistosomiasis. Parasitologists help prevent and treat these.
5. Immunology
Immunology focuses on how our bodies defend us against infections. This includes how vaccines work and why you feel feverish after an infection—it’s your immune system in action.
6. Microbial Genetics and Biotechnology
This involves studying the genes of microorganisms and using them to solve problems. For example, scientists can use bacteria to produce insulin for diabetic patients or even help clean up oil spills in the Niger Delta.
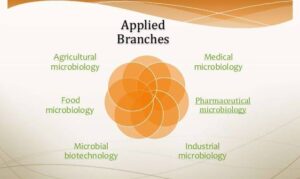
Applications of Microbiology
Now, how do all these branches help us in everyday life?
Health and Medicine: Microbiologists help diagnose diseases, create vaccines, and develop antibiotics.
Agriculture: Certain bacteria improve soil fertility. Others are used to control pests instead of harmful chemicals.
Food Industry: Microbes help in the production of foods like cheese, yoghurt, bread, ogi, and palm wine.

Environment: Microorganisms break down waste, clean polluted water, and even recycle nutrients in the soil.
Biotechnology: Microbes are used to make products like vitamins, biofuels, and even plastics that are friendly to the environment.
Summary
- Microbiology has several branches including bacteriology, virology, mycology, parasitology, immunology, and microbial genetics.
- Each branch focuses on different microbes and their roles.
- Microbiology is applied in health, farming, food processing, environmental care, and industry.
Evaluation
- Name any three branches of microbiology and explain what they study.
- Mention two ways microbiology helps in agriculture.
- How is microbiology useful in the food industry?
You’re learning things that many people never fully understand. Keep going—Afrilearn is proud of you, and the world needs bright minds like yours to make life better for everyone. Keep shining, and see you in the next lesson!
