Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 300 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hey champion! It’s great to see you again, ready to learn and grow your knowledge in microbiology. Today’s lesson is one you’ll find super interesting and practical—Classification of Parasites: Protozoa vs. Helminths. Now, parasites are those sneaky organisms that live off another living thing, like a thief that eats your food while pretending to be your friend! But not all parasites are the same, and today, we’ll get to know the two main types—protozoa and helminths—and how to tell them apart.
Classification Of Parasites: Protozoa Vs. Helminths
So let’s start with the big idea: A parasite is any organism that lives in or on another organism (called the host), feeding on it and sometimes causing harm. In our case, we’re focusing on parasitic organisms that affect humans, especially in Nigeria and other parts of Africa where some of these parasites are still common.
Imagine having an uninvited visitor who not only refuses to leave your house but eats your food, damages your belongings, and even makes you sick—that’s what parasites do to our bodies. Some are tiny and microscopic, others are long and worm-like. These differences help us classify them into two major groups.
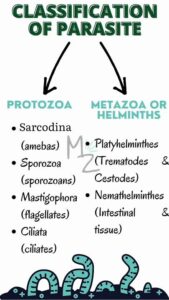
Protozoa
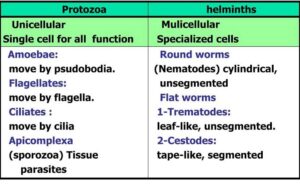
Protozoa are microscopic, single-celled organisms that can move and multiply quickly inside the human body. They often live in the blood, intestines, or tissues and are usually spread through contaminated food, water, or insect bites.
Examples of protozoa and the diseases they cause:
Plasmodium spp. – causes Malaria, spread by mosquitoes.
Entamoeba histolytica – causes Amoebic dysentery, spread through dirty water and food.
Giardia lamblia – causes Giardiasis, a diarrhoeal illness.
Trypanosoma brucei – causes Sleeping sickness, transmitted by the tsetse fly.
Key Features of Protozoa:
Unicellular (one-celled).
Can move using structures like cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia.
Multiply inside the host rapidly.
Often require microscopic examination for diagnosis.
Helminths
Helminths are multicellular worms—they are larger and can often be seen without a microscope. Some look like spaghetti, others like ribbons. They live in the intestines or other organs and feed on nutrients from the host. They reproduce by laying eggs that are passed out in faeces.
Examples of helminths and the diseases they cause:
Ascaris lumbricoides – causes Ascariasis, a roundworm infection.
Taenia spp. – causes Taeniasis, a tapeworm infection.
Schistosoma spp. – causes Schistosomiasis, a blood fluke infection.
Enterobius vermicularis – causes Pinworm infection, especially in children.
Key Features of Helminths:
Multicellular, larger than protozoa.
Can be round (nematodes), flat (trematodes), or segmented (cestodes).
Lay eggs which can be seen in stool samples.
Don’t multiply in the host the way protozoa do—rather, they grow and produce eggs.
Imagine protozoa as tiny, invisible pickpockets—they sneak in, multiply fast, and cause sudden illnesses like malaria or diarrhoea. Helminths, on the other hand, are like giant squatters in your house. They move in slowly, take up space in your intestines, and feed off your meals. You might not even notice them at first, but over time, they cause damage by stealing nutrients or blocking body passages.
Summary
- Parasites can be classified into protozoa and helminths.
- Protozoa are microscopic, single-celled organisms that multiply in the host and cause diseases like malaria and amoebiasis.
- Helminths are large, multicellular worms like roundworms and tapeworms that grow and lay eggs in the body.
- Protozoa are diagnosed through blood or stool microscopy, while helminths are usually found through stool tests or visible symptoms.
Evaluation
- What is a parasite?
- How are protozoa different from helminths?
- Name two protozoa and the diseases they cause.
- Give two examples of helminths common in Nigeria.
- Which parasite causes malaria?
You did it again! You’re learning things that will not only help you pass your exams but will also equip you to help your community. You now understand the two major types of parasites that affect humans—and that’s a big win! Keep asking questions, stay curious, and remember—Afrilearn is always cheering you on as you grow smarter, stronger, and more confident. See you next class, superstar!
