Back to: ZOOLOGY 200 Level
WELCOME TO CLASS
Today’s lesson is a fascinating journey into how animals—especially insects and other invertebrates—communicate, attract mates, and find their way across long distances. We’ll be looking at courtship, pheromones, migration, and the use of sound and visual signalling in the animal world. These behaviours help animals survive, reproduce, and interact with their environment effectively.
Courtship, Pheromones, Migration, Sound And Visual Signaling
Courtship
Courtship refers to the set of behaviours animals perform to attract a mate. It is especially important in insects, birds, and other animals to ensure that mating occurs between members of the same species. These behaviours can include dancing, displaying body parts like colourful wings or legs, or producing sounds.
For example, in many species of butterflies and moths, males flutter around females showing off their wing colours. In praying mantises, the male cautiously approaches the female while performing subtle movements to show he is a suitable mate and not food!
Pheromones
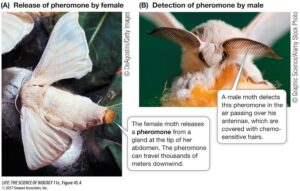
Pheromones are chemicals secreted by animals to send messages to others of the same species. These messages can relate to mating, marking territory, warning of danger, or identifying individuals.
In insects like ants, pheromones are key to communication. Worker ants leave a trail of pheromones to lead others to a food source. In moths, females release sex pheromones into the air to attract males from long distances. These scent signals are powerful and precise, ensuring that the right partners find each other.
Migration
Migration is the large-scale movement of animals from one location to another, usually linked to seasonal changes, breeding, or food availability. While it is common in birds and fish, some invertebrates also migrate.
For instance, the Monarch butterfly travels thousands of kilometres from Canada and the United States to Mexico every year. Despite their delicate wings, they manage this journey with the help of the wind, sun, and internal biological clocks. Migration helps them escape harsh weather and find better breeding conditions.
Sound and visual signalling
Animals often use sound and visual displays to communicate. Crickets and grasshoppers produce chirping sounds by rubbing their wings or legs together, especially to attract mates. These sounds are specific to each species and help individuals find suitable partners.
Fireflies are another great example of visual signalling. At night, males flash patterns of light to attract females, who respond with their own flashes. Each species has a unique light pattern, which ensures that the right individuals meet.

Summary
- Courtship behaviours help animals attract suitable mates through movement, colour, and sounds.
- Pheromones are chemical signals used in communication, especially for attracting mates or marking paths.
- Migration involves long-distance movement to improve chances of survival and reproduction.
- Sound and visual signalling are used by animals like crickets and fireflies for communication, especially during mating.
Evaluation
- What is the purpose of courtship in animals? Give one example.
- How do pheromones help ants or moths communicate?
- Describe migration and name one invertebrate that migrates.
- Give an example of sound and visual signalling in invertebrates.
Your curiosity and effort are helping you uncover how even the tiniest creatures live fascinating and intelligent lives. Keep asking questions and pushing forward. Afrilearn is with you every step of the way—ready for the next adventure!
