Back to: ZOOLOGY 200 Level
You’re doing absolutely well, and today we have something both fascinating and practical. We’re going to study the earthworm—not just what it looks like on the outside, but what’s inside it and why it’s so important for our planet. Don’t worry—we’re keeping everything virtual, safe, and student-friendly!
Earthworm dissection and ecological roles
External and internal features of an earthworm
Earthworms have a long, soft, cylindrical body made up of many similar-looking segments. The body is covered in moist skin, which helps with breathing since they absorb oxygen through it. You’ll notice a thick band around some middle segments—that’s called the clitellum. It plays an important role in reproduction.
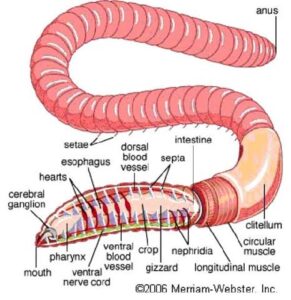
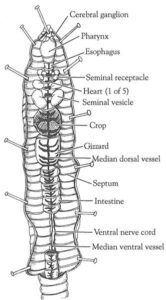
When virtually dissecting an earthworm, the internal structures reveal a well-organised system:
- The digestive system starts from the mouth and includes the pharynx, oesophagus, crop, gizzard, and intestine. The gizzard helps grind food, and the intestine digests and absorbs nutrients.
- The circulatory system is closed, with blood moving through vessels. There are five pairs of “hearts” that pump blood.
- The nervous system includes a nerve cord and ganglia (clusters of nerve cells).
- The excretory system has nephridia in most segments to remove waste.
Even though earthworms are simple, they have all the basic systems needed for life—how amazing!
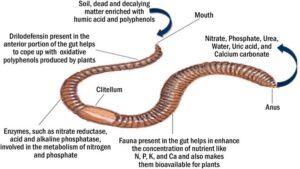
Ecological roles of earthworms
Earthworms are sometimes called “nature’s ploughs” because of how they help improve soil quality. As they burrow, they loosen the soil, making it easier for air and water to pass through. This helps plant roots grow better.
Their feeding habits also help recycle nutrients. Earthworms eat decaying organic matter like dead leaves and plant materials. After digestion, they excrete nutrient-rich castings (worm poop) that improve soil fertility—something every farmer loves.
In Nigeria, especially in farming communities, healthy earthworm populations are a sign of good soil. They’re a big reason crops like cassava, yam, and maize grow well in certain regions. Without them, soils can become compact and less productive.
Summary
Earthworms have simple but efficient body systems that support life and reproduction. Their ecological roles—like soil aeration, nutrient recycling, and promoting healthy plant growth—make them one of nature’s most helpful creatures.
Evaluation
- Name two internal organs found in an earthworm and their functions.
- What is the function of the clitellum in earthworms?
- How do earthworms help improve soil quality?
- Why are earthworms considered important to farmers?
Understanding creatures like the earthworm helps us see how even the smallest animals play a big part in keeping the world in balance. Keep your focus sharp and your heart open to learning—Afrilearn is always here cheering you on. Ready for the next topic?
