Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 100 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
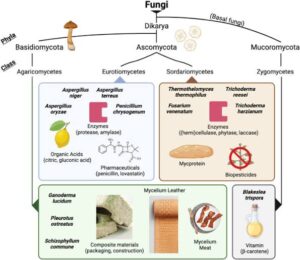
Hi there, bright star! It’s always exciting to learn with you, and today’s topic is one that connects deeply to our everyday life. We’re talking about the Economic Importance of Fungi—both the useful and the harmful ones. Yes, fungi are more than just the mushrooms you see in the market or the mould on old bread. They affect our food, health, agriculture, and even our wallets! Let’s find out how.
Economic Importance (Useful And Harmful Fungi)
Useful Fungi
Fungi can be very helpful. Here’s how:
Food Production
Some fungi are used to prepare food and drinks:

Yeast (like Saccharomyces cerevisiae) helps make bread rise and is used in brewing beer and wine.
Edible mushrooms are fungi too—they’re nutritious and delicious!
Medicine
Fungi are the source of many life-saving medicines:
The famous antibiotic Penicillin was discovered from the fungus Penicillium notatum. It has saved millions of lives.
Other fungi are used to produce drugs for treating high cholesterol and even cancer.
Agriculture
Certain fungi live in the soil and help plants grow:
Mycorrhizal fungi live in partnership with plant roots and help them absorb water and nutrients.
Some fungi act as natural pest killers (bio-control agents), helping farmers grow crops without harmful chemicals.
Industry
Fungi are used in many industries:
In the production of enzymes, organic acids, and vitamins.
In making soy sauce, cheese, and citric acid used in soft drinks.
Decomposition and Recycling
Fungi break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil. Without fungi, our environment would be full of waste!
Harmful Fungi
Not all fungi are good. Some can cause big problems:
Diseases in Humans
Candida albicans causes yeast infections.
Aspergillus can affect people with weak immune systems.
Ringworm and athlete’s foot are also fungal infections.
Plant Diseases
Fungi can destroy crops and affect food supply:
Puccinia causes rust disease in wheat.
Phytophthora infestans causes potato blight (it caused famine in some parts of the world!).
Food Spoilage
Fungi like moulds grow on bread, fruits, and leftovers when not properly stored. This leads to wastage.
Toxin Production
Some fungi produce poisons called mycotoxins.
Aspergillus flavus produces aflatoxins, which can contaminate stored grains like maize and groundnuts and are very dangerous to health.
Think of fungi like neighbours. Some bring you food or help with chores (useful fungi), while others damage your roof or steal your crops (harmful fungi). Knowing who’s who helps you protect yourself and get the best from them.
Summary
- Fungi are important in food production, medicine, agriculture, and the environment.
- Useful fungi include yeasts, mushrooms, and penicillin-producing fungi.
- Harmful fungi cause diseases in humans and plants, spoil food, and produce dangerous toxins.
- Understanding fungi helps us benefit from the good ones and manage the harmful ones.
Evaluation
- Name two useful roles of fungi in the food industry.
- What medicine is made from Penicillium?
- Give one example of a harmful fungus to crops.
- What are mycotoxins, and why are they dangerous?
- How do fungi help in nature?
You’ve just discovered how fungi can be both friends and foes. Keep your curiosity alive because every lesson is a step closer to becoming a microbiology genius. Afrilearn is proud of you—keep going strong!
