Back to: Environmental Biology 100 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello great learner! I’m so happy to have you here today. We are going to talk about something that explains how life on Earth is organised and connected. This topic is called Ecosystem Concepts, and trust me, it is something you experience every single day even if you don’t notice it. Let’s get started!
Ecosystem Concepts
Imagine you are standing in a large forest in Cross River or a riverbank in Niger State. You will see trees, birds, insects, fish, water, soil, and even feel the sunlight on your skin. All these things are connected and work together to support life. This connection forms what we call an ecosystem.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a natural system where living things (plants, animals, and microorganisms) interact with non-living things (soil, water, air, sunlight, and temperature) in a particular place. These interactions make life possible.
For example, think of a rice farm in Ebonyi State. The rice plants, farmers, water in the irrigation channels, fish in the water, and even the earthworms in the soil all make up an ecosystem. They depend on each other to survive.
Components of an Ecosystem
An ecosystem has two major parts:
1. Biotic Components
These are the living things in the ecosystem. They include:
* Plants (producers that make food using sunlight)
* Animals (consumers that eat plants or other animals)
* Microorganisms like fungi and bacteria (decomposers that break down dead matter and return nutrients to the soil)
For example, in a Nigerian savanna, grasses act as producers, antelopes as consumers, and fungi in the soil as decomposers.
2. Abiotic Components
These are the non-living things in the ecosystem that support life. They include:
* Sunlight
* Water
* Air
* Soil
* Temperature
Without these, living things cannot survive. For example, plants need sunlight for photosynthesis and soil to grow.
Types of Ecosystems
There are different kinds of ecosystems:
Terrestrial ecosystems (land-based) like forests, grasslands, and deserts
Aquatic ecosystems (water-based) like rivers, lakes, and oceans
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
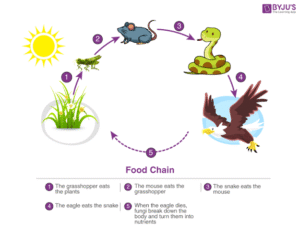
The main source of energy in an ecosystem is the sun. Plants capture sunlight and make food, which is then eaten by animals. This energy is passed along through food chains and food webs. Without energy flow, life would not continue.
Balance in an Ecosystem
Every organism in an ecosystem has a role to play. If one part is destroyed, it can affect the whole system. For instance, if too many trees are cut down in a forest, animals will lose their homes, the soil will erode, and the climate will change.
Summary
An ecosystem is the relationship between living and non-living things in a given area. It has two main components: biotic (living things) and abiotic (non-living things). Energy flows from the sun to plants and then to animals, creating balance in nature.
Evaluation
1. What is an ecosystem?
2. Mention three examples of biotic components and three abiotic components.
3. Name two types of ecosystems and give one example of each.
You’ve done excellently! Remember, the more you understand ecosystems, the better you can protect them. Keep learning with Afrilearn—you’re on your way to becoming an environmental hero. See you in the next class!
