Back to: BASIC SCIENCE JSS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the family trait. Enjoy the class!
Family Trait
Gregor Mendel experiment
Gregor Mendel was a monk and he experimented on garden pea plant in the garden of the monastery where he lived. He artificially crossbreeds a red garden pea flower (RR) with a white garden pea flower (rr). The product of this crossbreeding (offspring) all appears to be red, which means the red colour is dominant and the white colour is recessive. The products of Gregor Mendel’s experiment is referred to as the F1 generation.
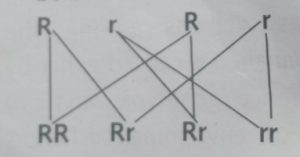
Gregor Mendel’s cross-breeding can be illustrated as shown below:

F1 generation. The phenotypic ratio is 100%.
To get the F2 generation, we will have to cross-breed the F1 generation as shown below.
For F2, the phenotypic ratio is 3:1, and the genotypic ratio is 1:2:1.
Importance of family traits
Importance of family traits includes:
- Intelligence: Parents with high intelligence quotient mostly give birth to intelligent offspring. This type of trait seems to be continuous from one generation to another.
- Disease: With adequate knowledge of genetics, many genetic diseases can be prevented from being transferred from parents to offspring. Prospective couples are counselled to ascertain their genetic make-up before going into marriage to avoid transmitting diseases. Unlike in the past when people go into marriage without knowing their genetic make-up, which usually led into passing their genetic diseases such as albinism, sickle cell anaemia, colour blindness, down from one generation to another due to inadequate knowledge of Genetics.
- Resemblance: Resemblance is a very common family trait which helps to identify members of a family.
- Family genealogy: The knowledge of family trait makes it easy to trace the ancestor of a family (lineage) and then use it to predict the present and future traits through the discovered traits.
- Knowledge of family traits helps in crime detection
Blood group and genotype
Blood group is also a very common family trait, there are four main types of blood group: A, B, AB, and O. If a man husband) has a blood group A, and woman (wife) has a blood group B, then there is a possibility that their offspring will have blood group A, B, AB or O.
The genotype is another factor to consider in family genealogy, there are four main types of genotype: AA, AS, SS, and AC.
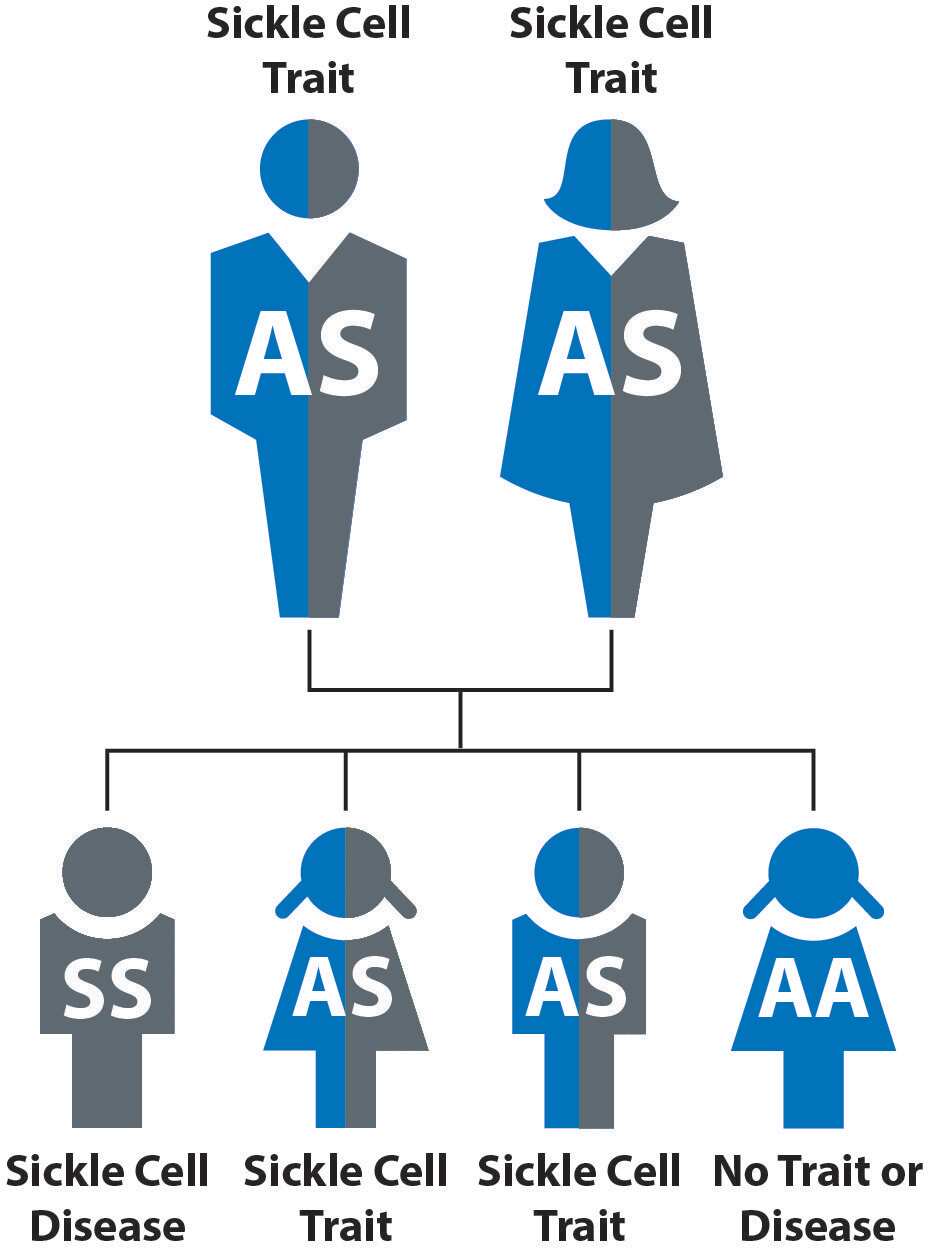
For example, if a man and a woman are both sickle cell carriers (AS) there is a possibility of producing normal offspring and a sickler as illustrated below:
Parent: AS and AS
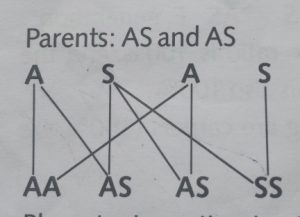
Phenotypic ratio is 3:1 while the genotypic ratio 1:2:1. 25%of the offspring are normal, 59% are carriers and 25% are sickles.
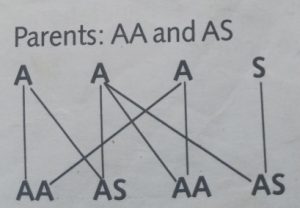
phenotypic ratio is 100% while the genotypic ratio is 1:1. 50%of the offspring are normal while the other 50% are carriers.
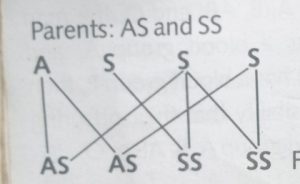
The phenotypic ratio 1:1 and the genotypic ratio is also 1:1. 50% of the offspring are a carrier and 50% are sicklers.
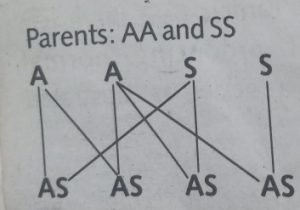
The phenotypic ratio is 100% and the genotypic ratio is 100%. All the offspring are a carrier (100% are carrier).
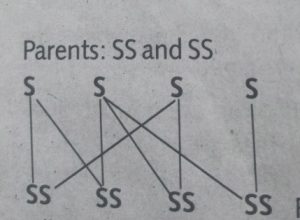
All offspring are sicklers.
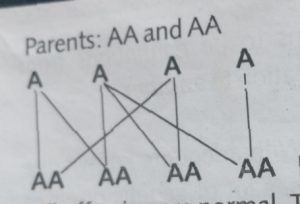
All offspring are normal. The phenotype is 100% and the genotype is also 100%.
Family tree
A family tree or pedigree is a diagram that represents the relationship among families, i.e. relationships between parents and their offspring from one generation to another. The first generation includes their children; the second generation includes their grandchildren, etc.
A family tree consists of both horizontal and vertical lines that show the relationship between the father and mother, their children and their successive generation. The family tree can be used to trace the generation of the parents or can be used to trace the generation of either the father alone of that of the mother alone.
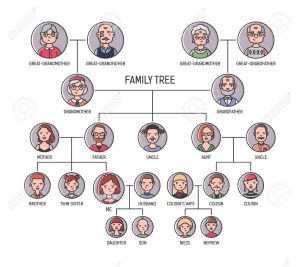
Types of family
There are two main types of family, they are:
- Nuclear family
- Extended family
Will break it down so you will understand better;
Nuclear family:
This is a type of family that involves the man (husband), the woman (wife/wives) and their child/ children. This type of family can be further divided into:
- Monogamous family
- Polygamous family
- Polyandry family
Monogamous family: This consists of the man (husband), the woman (wife) and child/children. In this type of family, the child/children receive(s) their stability from the husband and wife. A monogamous family is mostly practised in the Western world.
Polygamous family: This consists of a man (husband) and multiple wives. Polygamous family is mostly practised in Africa.
Polyandry family: This is another type of polygamous family, which consists of a woman and multiple husbands. This family type is common in some parts of India.
Extended family:
This consists of relatives (cousins, uncles, aunties) living in the same home with a man (father), the woman (mother), and the children.
In our next class, we will be talking about Environmental Hazard – Soil Erosion. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

please I don’t understand how to crossbreed it
I don’t understand how to crossbteed them
just move from the first trait to the second
just move from the first trait to the second
The cross breeding is hard to understand. Do you go guys understand? 😞😞
ANOTHER FAMILY TRAIT
We’re glad you found it helpful😊 For even more class notes, engaging videos, and homework assistance, just download our Mobile App at https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.afrilearn. It’s packed with resources to help you succeed🌟
I really gained alot from this lesson
please what is family trait
Thank you very much
Due to my knowledge,family trait is a characteristic been passed from parents to their offspring