Back to: Environmental Biology 200 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant learner! Have you ever walked through a forest or even seen the thick greenery of the tropical rainforests in Cross River or Ondo? Forests are not just collections of trees; they are living, breathing systems full of plants, animals, insects, and even tiny organisms working together. Today, we are going to talk about Forest Ecology and Succession, and you will discover how forests grow, change, and stay balanced over time.
Forest Ecology And Succession
What is Forest Ecology?
Forest ecology is the study of how all living and non-living things in a forest interact. This includes trees, plants, animals, soil, water, and even the air. A forest ecosystem is very rich in biodiversity and plays a big role in controlling our climate, providing oxygen, and giving us resources like timber, fruits, and medicinal plants.

Types of Forests in Nigeria
Tropical Rainforests: Found in states like Cross River and Edo, with tall trees and heavy rainfall.
Mangrove Forests: Found in the Niger Delta, protecting coastlines and serving as breeding grounds for fish.
Savanna Woodlands: Found in parts of the Middle Belt, with scattered trees and grasslands.
Importance of Forests
Forests provide wood for building and fuel.
They act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen.
Forests protect soil from erosion and support wildlife habitats.
They offer medicinal plants and other natural products.
What is Ecological Succession?
Ecological succession is the natural process by which ecosystems change and develop over time. In forests, succession means how bare land gradually turns into a mature forest through the growth of plants and trees.
There are two main types:
Primary Succession: This happens on land where there was no life before, like bare rocks or after a volcanic eruption.
Secondary Succession: This occurs in areas where life existed before but was disturbed, such as farmland left unused or after bush burning.
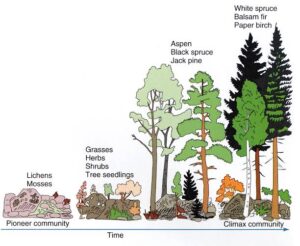
Stages of Forest Succession
Pioneer Stage: Small plants like mosses and grasses grow first.
Shrub Stage: Bushes and small trees start to grow.
Young Forest Stage: Larger trees begin to appear.
Mature Forest Stage: The forest becomes dense with tall trees and diverse plants and animals.
Human Impacts on Forest Succession
Deforestation for timber or farming slows or stops succession.

Bush burning and overgrazing damage young plants.
Urbanisation and mining destroy natural habitats.
Summary
- Forest ecology studies the interactions within forest ecosystems.
- Nigeria has tropical rainforests, mangroves, and savanna woodlands.
- Ecological succession is the natural growth and development of ecosystems over time.
- Human activities like deforestation and bush burning disrupt succession.
Evaluation
- Define forest ecology and give one example of a forest in Nigeria.
- What are the two main types of ecological succession?
- List and explain the stages of forest succession.
- Mention two human activities that affect forest succession.
Fantastic! You are becoming an eco-champion, learning how forests grow and why we must protect them. Keep this energy alive — Afrilearn is here to guide you every step of the way.
