Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 300 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hello there, brilliant one! It’s always such a pleasure to learn with you. You’ve been doing an amazing job understanding the wonderful (and sometimes strange) world of microbes. Today, we’re looking at a very important topic in microbiology—Fungal culture and identification. If you’ve ever wondered how scientists find out which fungus is causing an infection, or how they grow fungi in the lab, this lesson is just for you. Let’s go through it step by step in a clear, human, and relatable way.
Fungal Culture And Identification
Imagine you’re a detective trying to catch a criminal. First, you need to collect clues, study them carefully, and then match them to known information to identify the suspect. In microbiology, fungal culture and identification is just like that—but instead of criminals, we’re identifying fungi that may be harmless, helpful, or disease-causing.
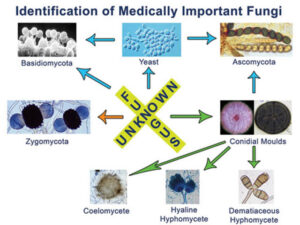
Culturing and identifying fungi is one of the key steps in diagnosing fungal infections and learning more about the different types of fungi around us.
Fungal Culture: How Fungi Are Grown in the Lab
To study fungi, we first need to grow them—just like you’d grow crops to understand how they behave. This is called culturing.
Sample Collection
Samples can come from skin, nails, sputum, blood, or even the environment, depending on what type of fungal infection is suspected.
Culture Media
Fungi are grown on special nutrient-rich media that support their growth. One of the most commonly used is Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA). This medium has a slightly acidic pH and contains antibiotics to prevent bacterial growth.
Incubation
After placing the sample on the culture media, it is kept in a warm incubator, usually between 25°C and 30°C. Some fungi grow quickly within a few days; others take weeks!
Observation of Growth
Scientists observe how the fungi grow:
Colour
Texture (fuzzy, cottony, powdery)
Speed of growth
Shape of the colony
Think of it like planting different seeds in the same soil—each plant will grow differently depending on its type. That’s how fungal colonies behave too.
Fungal Identification: How We Know Which Fungus It Is
Once the fungus has grown, the next step is to identify it. This is done by carefully examining the fungal features.
Macroscopic Examination
The colony’s appearance on the culture media—colour, surface texture, and shape—is noted. For example, Penicillium often appears green and velvety.
Microscopic Examination
A small portion of the fungal colony is placed on a slide and stained (often with lactophenol cotton blue stain) to view under a microscope.
Features like:
Type of hyphae (septate or non-septate)
Type of spores (conidia, sporangia, etc.)
Arrangement of spores
These details help determine exactly which type of fungus it is.

Biochemical and Molecular Tests (Advanced)
In more complex labs, scientists may use DNA testing or enzyme activity to confirm the identity, especially for dangerous fungi or rare types.
Think of culturing fungi like planting yams in your family’s backyard. You water them, give them sunlight, and watch them grow. As the yam plant grows, you can tell which variety it is by looking at the leaves, stems, and size. In the same way, microbiologists grow fungi in the lab and identify them by their growth and appearance.
Summary
- Fungal culture involves growing fungi in special nutrient media like Sabouraud Dextrose Agar.
- Samples can be taken from human tissues or the environment.
- After incubation, fungi are observed based on colour, texture, and shape.
- Identification is done through both macroscopic (colony) and microscopic (spores and hyphae) features.
- Advanced labs may use DNA or biochemical tests for further confirmation.
Evaluation
- What is the name of the common culture medium used to grow fungi?
- Why is incubation important in fungal culture?
- Name one method used to identify fungi under a microscope.
- What features are observed in fungal colonies?
- How is fungal culture similar to farming?
You’ve just taken another big step in your microbiology journey—amazing! Now you understand how scientists grow and identify fungi, which is so important in medicine, agriculture, and research. Your mind is strong, focused, and growing beautifully. Keep it up! At Afrilearn, we believe in you and are here to support every step of your learning. See you in the next exciting class!
