Back to: Environmental Biology 200 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello bright star! I’m excited to have you here today. Have you ever walked through a swampy area or seen the big mangroves in the Niger Delta? Did you notice how alive those areas are — full of fish, crabs, and birds? That’s because wetlands are like nature’s supermarkets and water cleaners! Today, we’ll learn about Hydrology & Wetland Ecosystems — and by the end of this class, you’ll understand why water and wetlands are so important for life in Nigeria and beyond.
Hydrology & Wetland Ecosystems
What is Hydrology?
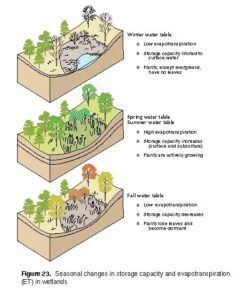
Hydrology is the study of water — how it moves, where it comes from, and how it’s stored on Earth. Water is everywhere: in rivers like the River Niger, in underground wells, in rainfall, and even in the air. Hydrology helps us understand how water supports life, prevents droughts, and shapes our environment.
The Water Cycle
The water cycle explains how water moves around our planet:
Evaporation: Heat from the sun turns water from rivers, lakes, and oceans into vapour.
Condensation: The vapour cools and forms clouds.
Precipitation: Water falls as rain, hail, or snow.
Collection: Water gathers in rivers, lakes, wetlands, and underground.
In Nigeria, this cycle is vital for agriculture — the rains that help rice fields in Kebbi or yam farms in Benue come from this natural cycle.
What are Wetland Ecosystems?
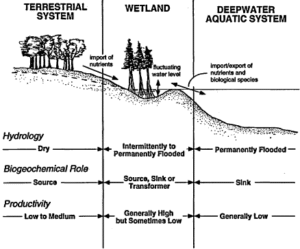
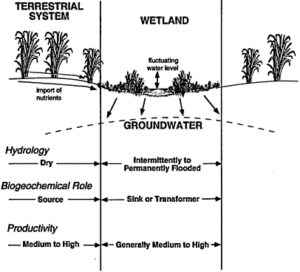
Wetlands are areas where water covers the soil or is present near the surface for most of the year. Examples include swamps, marshes, floodplains, and mangroves. In Nigeria, we have wetlands in places like the Hadejia-Nguru wetlands in the north and the mangroves of the Niger Delta.
Importance of Wetlands
Home to wildlife: Fish, crabs, crocodiles, and birds like herons live in wetlands.
Flood control: Wetlands act like sponges, soaking up extra water during heavy rains.
Water purification: Wetlands filter dirt and pollutants, keeping water clean.
Livelihoods: Many Nigerians rely on wetlands for fishing, farming, and gathering firewood.
Climate regulation: Wetlands trap carbon, helping reduce climate change effects.
Human Activities and Wetlands
Sadly, many wetlands are being drained or polluted. Oil spills in the Niger Delta, overfishing, or building houses on wetlands destroy these important ecosystems. Protecting wetlands is key for our future — planting mangroves, avoiding waste dumping, and creating laws can help.
Summary
- Hydrology is the study of water and its movement.
- The water cycle explains how water moves through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection.
- Wetlands are water-rich ecosystems like swamps and mangroves.
- Wetlands provide homes for wildlife, control floods, clean water, and support livelihoods.
Evaluation
- What is hydrology?
- List and explain the four main stages of the water cycle.
- Mention three types of wetlands found in Nigeria.
- Why are wetlands called “nature’s sponge”?
You did wonderfully today! Remember, water is life, and wetlands are one of nature’s greatest treasures. Every time you see a river or swamp, think of the life it supports. I’m looking forward to our next exciting lesson with Afrilearn!
