Back to: ZOOLOGY 200 Level
WELCOME TO CLASS
Let’s talk about two important structural features found in many animals—segmentation and the exoskeleton. These two may sound like technical terms, but they play a huge role in how animals move, protect themselves, and survive in different environments. Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand and easy to remember.
Importance Of Segmentation And Exoskeleton
Segmentation improves body function
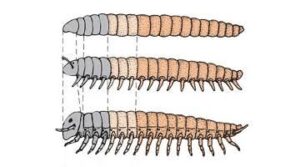
Segmentation means dividing an animal’s body into repeated parts or sections, called segments. Animals like earthworms, centipedes, and even humans show segmentation. In earthworms, for instance, each segment contains muscles and nerves, allowing for coordinated and flexible movement. If you’ve ever watched an earthworm wiggle through soil, you’ve seen segmentation in action!
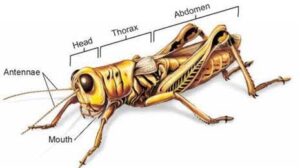
Segmentation also allows different body parts to take on special roles. In insects, the body is divided into three main segments—head, thorax, and abdomen. Each segment has a unique function, which helps the animal to move efficiently, find food, and respond quickly to its surroundings.
Segmentation aids survival and regeneration
Segmentation doesn’t just help with movement—it can also help with survival. In some segmented animals, if part of the body is damaged or cut off, they can regenerate the lost segment. This is seen in certain worms and arthropods. It also means that damage to one part may not affect the rest of the body as severely, increasing the animal’s chances of survival.
The exoskeleton protects the body
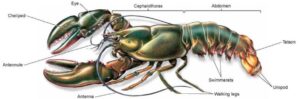
The exoskeleton is a hard, outer covering found in animals like insects, crabs, and millipedes. Think of it as a strong suit of armour. It provides protection from physical injury, prevents water loss (especially important for land-dwelling insects), and supports the animal’s body.
Unlike our internal skeletons, the exoskeleton is on the outside, which also means it must be shed from time to time for the animal to grow—a process called moulting. Have you ever seen an empty insect shell on the ground? That’s the old exoskeleton left behind after moulting.
The exoskeleton helps movement
The exoskeleton isn’t just about protection. It also provides anchorage for muscles, allowing insects and crustaceans to move with precision and power. For example, a grasshopper’s strong legs are supported by its exoskeleton, allowing it to jump great distances relative to its size.
Summary
Segmentation allows flexible, efficient movement, helps with survival and regeneration, and gives body parts specialised functions. The exoskeleton protects the animal, supports the body, prevents water loss, and works with muscles to allow movement. Together, these features help animals adapt to different environments and challenges.
Evaluation
- What is segmentation and why is it important in animals?
- Name two animals that have segmented bodies.
- What are two major functions of the exoskeleton?
- Describe the process of moulting.
You’ve just explored how two special features—segmentation and exoskeleton—give animals the strength, movement, and survival tools they need. Stay inspired and stay curious! Afrilearn is here to guide you every step of the way. Let’s keep going!
