Back to: ZOOLOGY 500 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello there, future environmental game-changer! I’m truly excited you’re here today because we’re unlocking a powerful tool that is shaping the future of ecology—not just in Nigeria but all over the world. Today’s topic is Introduction to GIS in Ecological Studies. Now, don’t let the abbreviation scare you. By the end of this class, you’ll see just how useful and even exciting GIS can be in helping you understand, protect, and manage the environment.
Introduction To GIS In Ecological Studies
What is GIS?
GIS stands for Geographic Information System. It’s a computer-based tool that helps you capture, store, analyse, and display geographic (location-based) data. In simple terms, GIS helps you make maps and draw conclusions from them.
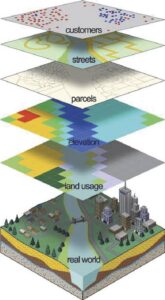
Imagine being able to sit in a classroom or your home in Ibadan and use your laptop to see the distribution of elephants across Nigeria, track deforestation in Ogun forests, or identify potential habitats for endangered birds in Jos. That’s the power of GIS.
Why is GIS Important in Ecology?
Ecological studies are deeply tied to location. Animals don’t just live—they live somewhere. Plants don’t grow in isolation—they grow in certain soils, under certain conditions, in certain areas. GIS helps ecologists:
Map species distribution
Monitor habitat loss or changes
Track animal movement and migration
Plan conservation areas and wildlife corridors
Analyse the impact of human activities on ecosystems
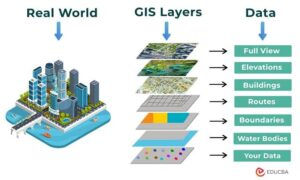
Basic Components of GIS
Hardware: Your computer, GPS devices, drones, or tablets
Software: Programs like ArcGIS, QGIS, or Google Earth
Data: This includes satellite images, field-collected data (like animal sightings or soil type), or topographic maps
People: Trained users like you—ecologists, conservationists, researchers
Real-Life Example from Nigeria
Let’s say scientists in Taraba want to monitor changes in savannah grasslands caused by farming. Using GIS, they can compare satellite images from the past five years, identify areas of vegetation loss, and plan interventions. That’s smarter and faster than walking the entire land physically.
How Ecologists Use GIS
Habitat Suitability Modelling: Predict where a species is likely to thrive based on environmental factors
Change Detection: Compare maps from different years to track forest cover loss or flooding
Wildlife Tracking: Plot GPS data from collars worn by elephants or lions to study movement patterns
Mapping Ecological Zones: Define where wetlands, mangroves, rainforests, and drylands exist in a region
Challenges and Considerations
While GIS is powerful, it’s not perfect. It depends heavily on the quality of data you input. Poor data = poor results. Also, it requires training to use effectively, though many free resources now exist online.
Summary
- GIS stands for Geographic Information System—a tool for mapping and spatial analysis
- It helps ecologists monitor species, habitats, and human impact
- Core components include hardware, software, data, and trained users
- GIS supports decision-making in conservation and ecosystem management
- Tools like ArcGIS and QGIS are commonly used in ecological studies
Evaluation
- In your own words, what is GIS and why is it useful in ecology?
- List two Nigerian ecological problems that GIS can help solve.
- What are three components of a GIS system?
- Describe one real-life way you could use GIS as a zoologist in Nigeria.
You’re not just learning to read maps—you’re learning to change the future with data and insight! With tools like GIS, you’re preparing to make real impact in the fight for a healthier, greener Africa. Keep shining and never forget—Afrilearn believes in your power to lead the change!
