Back to: BASIC SCIENCE JSS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about light energy. Enjoy the class!
Light Energy

Light is a form of energy, which can enable us to see. It is very essential and familiar to us. Light is electromagnetic radiation and it can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, absorbed by coloured objects and 6-travels at a speed of 3×108 m/s in a vacuum or space.
Reflection of light
Reflection of light is the sending back of light rays when it hits a surface. It can be regular or diffuse.
- Regular reflection: Reflection is said to be regular when light rays hit a smooth or highly polished surface and bounce off from it, as a parallel beam in the same opposite direction.
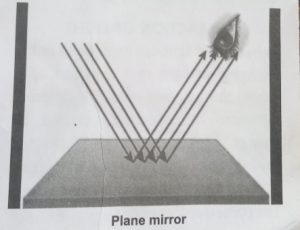
Regular reflection takes place from materials like glass, highly polished metal, oil, etc. A very good example of regular reflection can be seen in a mirror.
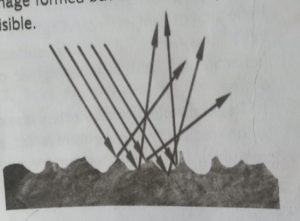
2. Diffuse reflection: Reflection is said to be diffuse or irregular when light rays hit a rough surface. The reflected rays will be scattered in different directions. Diffuse reflection takes place when light rays are incident on a surface like a wall, a piece of wool, a leaf of a tree, etc. In diffuse reflection, there is no definite Image formed but the surface becomes visible.
Refraction of light
Refraction of light can be defined as the changing of light rays direction as it passes through two media of different densities. This is mostly caused by a change in the speed of the light. The refracted ray is the bent ray as a result of passing from one optical medium to another.
The consequences of refraction include:
Real depth, apparent depth, refractive index and wavelength of light.
- Real depth: Real depth is the actual depth of an object in a medium.
- Apparent depth: Apparent depth the depth is depth in which a transparent medium such as water, glass, etc see to have after refraction of light rays Apparent depth explains why swimming pool or a river shallower than it is. An amateur or inexperience swimmer might be drowned in a pool of water or river simply because appears less deep than it is.
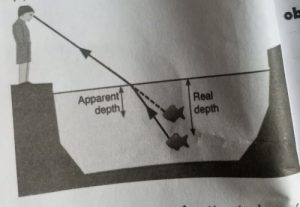
- Refractive index: Refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of light in air to speed of light in that substance.
n=speed of light in air/speed of light in a substance
Experiments can be used to demonstrate real and apparent depth to calculate the refractive index such medium.
Vision
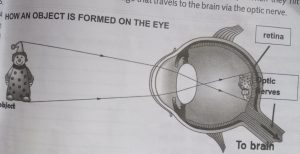
It is common knowledge that we see things with our eyes. Many parts of the eyes contribute to the vision. The light from the sun or artificial light travels in a straight line and bounces off the object and into our eyes through the pupil. The Iris changes the size of the pupil, depending on the amount/intensity of the light, to let more or less light into the eye. The light then passes through the lens and focused onto the back of the retina.
The retina covered in millions of light-sensitive receptors known as rods and cones.
Each receptor contains pigment molecules, which changes shape when they hit by light, triggering an electrical message that travels to the brain via the optic nerve.
How an object is formed on the eye
Dispersion and rainbow
Dispersion of light is the process of splitting a beam of light into seven constituent colours when passed through a glass prism or other transparent medium. Glass prisms, drops of water, and other transparent materials can split or disperse white light into seven components.
A spectrum of light is the result obtained when white light is spread into several colours. The colours are Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet (ROYGBIV).
Rainbow is a natural dispersion of light drops of water and dust in the atmosphere. A rainbow of seven colours is usually seen in the sky after rainfall when the sun is shining. After rainfall, a large number of water droplets now act as a prism that splits the sunlight into seven colours.
Colour of objects
When white light is incident on an object of colour, such as green, the green colour will be reflected/seen. This is because the green-ray in the incident light is reflected while all the other colours are absorbed.
On the other hand, when white light is incident on black material, all the colours of the incident light will be absorbed by the material, and thus, no colour will be reflected/seen. This is why black is not regarded as a colour. A white material will reflect all the colours of the incident light and white is seen.
In our next class, we will be talking about Sound Energy. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

Thanks this really helps me to understand the topic better