Back to: Environmental Biology 100 Level
Welcome to class!
Hello brilliant learner! Today’s lesson is a very interesting one because it takes us on a journey around the world without leaving your chair. Our topic is Major Biomes of the World, and by the end of this lesson, you will understand the different types of large ecosystems found on Earth and what makes each one special. Let’s begin!
Major Biomes Of The World
Imagine travelling from the Sahara Desert to the Amazon Rainforest, then to the icy lands of Antarctica. You will notice that plants, animals, and even the climate are different in each place. These large natural regions are called biomes. A biome is a large area on Earth with similar climate, plants, and animals.
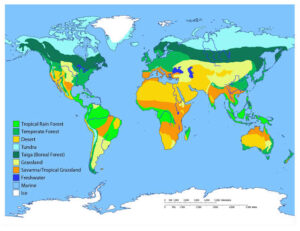
What is a Biome?
A biome is a major ecological community that covers a large area and is defined by its climate, vegetation, and animal life. The main factors that determine a biome are temperature, rainfall, and soil type.
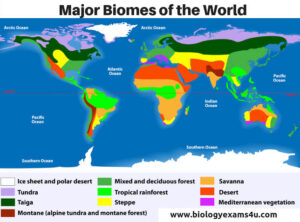
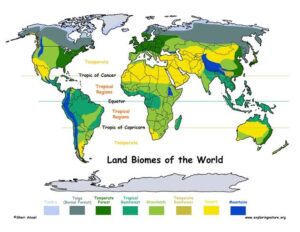
Major Biomes of the World
Tropical Rainforest
Location: Found near the equator in places like the Amazon (South America), Congo Basin (Africa), and parts of Nigeria (Cross River).
Climate: Hot and wet all year round.
Vegetation: Tall trees, thick forests, many layers of plants.
Animals: Monkeys, parrots, snakes, insects.
Importance: Provides oxygen, home to diverse species, source of medicine.
Savanna (Tropical Grassland)
Location: Found in Africa (Nigeria, Kenya), South America, and Australia.
Climate: Hot with a long dry season and a short rainy season.
Vegetation: Grasses with scattered trees like baobab and acacia.
Animals: Lions, elephants, zebras, antelopes.
Importance: Supports grazing animals and agriculture.
Desert
Location: Sahara (Africa), Arabian Desert, Kalahari Desert.
Climate: Very hot during the day, cold at night, little rainfall.
Vegetation: Cacti and drought-resistant plants.
Animals: Camels, snakes, scorpions.
Importance: Source of minerals and solar energy.
Temperate Grassland
Location: North America (prairies), Asia (steppes), South America (pampas).
Climate: Moderate rainfall, hot summers, cold winters.
Vegetation: Grasses, very few trees.
Animals: Bison, antelopes, wolves.
Temperate Forest
Location: Europe, North America, parts of Asia.
Climate: Mild summers, cold winters, moderate rainfall.
Vegetation: Deciduous trees like oak and maple.
Animals: Deer, foxes, bears.
Taiga (Boreal Forest)
Location: Canada, Russia, Scandinavia.
Climate: Very cold winters, short summers.
Vegetation: Coniferous trees like pine and spruce.
Animals: Moose, wolves, bears.
Tundra
Location: Arctic regions.
Climate: Extremely cold, little rainfall, frozen soil (permafrost).
Vegetation: Mosses, lichens, small shrubs.
Animals: Polar bears, arctic foxes, reindeer.
Aquatic Biomes
Marine: Oceans, seas (cover 70% of Earth).
Freshwater: Rivers, lakes, streams.
Animals: Fish, dolphins, plankton.
Importance of Biomes
They maintain the Earth’s climate.
They provide food, water, and raw materials.
They support biodiversity and life on Earth.
Summary
Biomes are large ecological regions defined by climate, vegetation, and animals. Major biomes include tropical rainforest, savanna, desert, temperate forest, grassland, taiga, tundra, and aquatic biomes. Each biome is unique and essential for life.
Evaluation
What is a biome?
Mention three characteristics of the tropical rainforest.
List four major biomes and one unique feature of each.
Fantastic work today! You’ve just toured the planet through its biomes without moving an inch. Keep learning with Afrilearn—you’re building knowledge that will change your world. See you in the next class!
