Back to: ZOOLOGY 200 Level
WELCOME TO CLASS
Today, we’re going to look at an incredible process in the animal kingdom: metamorphosis and insect development. These two phenomena are crucial for understanding how insects grow and evolve, and how they adapt to their environments over their life cycle. Let’s break down the stages of metamorphosis and the different ways insects develop.
Metamorphosis And Insect Development
What is Metamorphosis?
Metamorphosis is the biological process by which an insect undergoes a dramatic change in form and structure as it develops from one life stage to another. In insects, this transformation can be complete or incomplete, depending on the species. This process allows insects to adapt to different environments at different stages of their life.

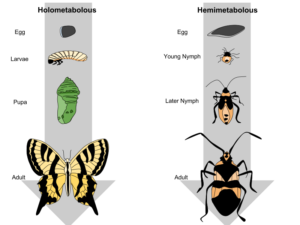
Complete Metamorphosis (Holometabolism)
In insects that undergo complete metamorphosis, the life cycle consists of four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage looks and behaves differently, allowing the insect to exploit different resources at each point in its life.
- Egg: The life of an insect begins as an egg laid by the adult female. Inside the egg, the embryo develops into a larvae.
- Larva: The larva is a juvenile form that is typically very different from the adult. This stage is often focused on feeding and growing. For example, caterpillars (the larvae of butterflies) eat leaves to grow large before entering the next stage.
- Pupa: After the larval stage, the insect enters the pupa stage, where it undergoes a complete transformation. This stage is usually inactive, and the insect is often encased in a protective cocoon or chrysalis (like a caterpillar turning into a butterfly).
- Adult: Finally, the adult emerges from the pupa, having fully developed wings and reproductive organs. The adult form is capable of reproduction and is often quite different from the larval stage. For example, a caterpillar becomes a butterfly, and a maggot becomes a fly.
Incomplete Metamorphosis (Hemimetabolism)
Some insects undergo incomplete metamorphosis, where the life cycle consists of three stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Unlike complete metamorphosis, there is no pupal stage in this process. The nymph is a smaller version of the adult and often looks like a miniature version of the adult but without fully developed wings and reproductive organs.
- Egg: The insect begins life as an egg, just like in complete metamorphosis.
- Nymph: After hatching, the insect enters the nymph stage. Nymphs resemble the adult but are often smaller, with underdeveloped wings and reproductive systems. As the nymph grows, it sheds its exoskeleton (a process known as moulting) several times, getting closer to the adult form with each shedding.
- Adult: Once the nymph has fully matured and grown wings (in species that have them), it becomes an adult insect, capable of reproduction.
Examples of insects that undergo incomplete metamorphosis include grasshoppers, cockroaches, and dragonflies.
Why is Metamorphosis Important?
Metamorphosis is an important adaptation for insects as it allows them to live in different environments and occupy different ecological niches at various stages of their development. For example, the larval and adult stages often have different diets, which reduces competition between the young and the adults. This strategy helps insects to maximise their survival and reproductive success.
For example, a caterpillar (the larval stage of a butterfly) might feed on leaves, while the adult butterfly feeds on nectar. This difference in diet prevents competition between the two stages.
Summary
- Metamorphosis is the process by which insects transform from one life stage to another.
- Complete metamorphosis includes the egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages.
- Incomplete metamorphosis includes the egg, nymph, and adult stages.
- Metamorphosis allows insects to exploit different resources at different stages of their life cycle.
Evaluation
- What are the four stages of complete metamorphosis, and what happens in each stage?
- How does incomplete metamorphosis differ from complete metamorphosis?
- Give an example of an insect that undergoes incomplete metamorphosis.
- Why is metamorphosis important for the survival of insects?
You’ve just taken a closer look at the fascinating process of metamorphosis and how it helps insects adapt and thrive. Great job, and keep up the excellent work! Stay curious and excited for the next lesson. You’re doing amazing!
