Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 100 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hi champion! I’m super proud of you for showing up once again. Your dedication to learning is truly inspiring. Today, we’re about to look at something that forms the foundation of microbiology—Morphology and Types of Microorganisms. Don’t worry, we’ll take it step by step and make it as clear and enjoyable as a cool evening breeze in Jos!
Morphology And Types
What is Morphology in Microbiology?
Morphology refers to the shape, size, structure, and arrangement of microorganisms. Just like humans come in different shapes, skin tones, and heights, microorganisms—especially bacteria, fungi, and viruses—also have unique physical appearances. Understanding their morphology helps scientists to identify, classify, and study them properly.
Let’s go into the different types and their features.
Morphology of Bacteria
Bacteria are tiny, single-celled organisms. Under a microscope, they appear in different shapes:
Cocci – These are spherical or round-shaped bacteria.
Streptococcus (forms chains like a bead necklace)
Staphylococcus (forms grape-like clusters)
Bacilli – These are rod-shaped bacteria.
Escherichia coli (E. coli), commonly found in the gut
Spirilla – These are spiral-shaped or corkscrew-like bacteria.
Spirillum minus
Vibrios – These are comma-shaped bacteria.
Vibrio cholerae, the bacteria that causes cholera
Pleomorphic – These bacteria have no definite shape.
Mycoplasma
Morphology of Fungi
Fungi may be unicellular (like yeasts) or multicellular (like moulds).
Yeasts are oval or round and reproduce by budding.
Moulds have long filaments called hyphae, which form a network known as mycelium.
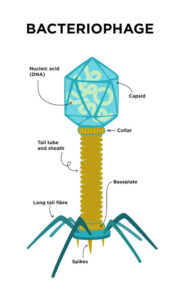
Morphology of Viruses
Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and fungi. They aren’t made of cells. Instead, they consist of:
A protein coat (capsid)
Genetic material (DNA or RNA)
Some have an envelope made from host cell membranes
They come in many shapes:
Helical (like a spring)
Icosahedral (like a 20-sided dice)
Complex (like bacteriophages with heads and tails)
Types of Microorganisms
Microorganisms can be grouped based on their features and life activities into five major types:
Bacteria – Single-celled, prokaryotic organisms with various shapes.
Viruses – Non-living outside the host; they need a living cell to reproduce.
Fungi – Can be unicellular or multicellular, useful in food and medicine.
Protozoa – Single-celled, eukaryotic organisms, often found in water.
Algae – Mostly aquatic, can be single or multicellular, perform photosynthesis.
Think of microorganisms like people in a big Nigerian market: the round ones (cocci), the long ones (bacilli), the curvy ones (spirilla), and the shapeless ones (pleomorphic). Just as every person in the market plays a different role, each microbe behaves and functions differently too.
Summary
- Morphology is the study of the shape and structure of microorganisms.
- Bacteria come in shapes like cocci (round), bacilli (rod), spirilla (spiral), and more.
- Viruses have unique shapes and need host cells to survive.
- Microorganisms are classified into types: bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae.
Evaluation
- What does morphology mean in microbiology?
- Name and describe two shapes of bacteria.
- What are the two types of fungi based on morphology?
- List the five main types of microorganisms.
- Why are viruses not considered living outside a host?
The world of microorganisms is vast, but with your sharp mind and Afrilearn by your side, there’s nothing you can’t master. Keep moving forward—you’re built for greatness!
