Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 300 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
It’s great to have you back! Today we’re focusing on a topic that’s both important and very real in everyday life—Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), particularly Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, and Syphilis. These infections are far more common than most people realise, especially among young adults in Nigeria and across Africa. They don’t just affect the body—they can also impact relationships, fertility, and future well-being. Understanding them is key to public health and personal safety.
Stis: Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Syphilis
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most widespread STIs and is often transmitted through unprotected vaginal, oral, or anal sex.
Symptoms:
In men: Burning during urination, white/yellow discharge from the penis, swollen testicles.
In women: Increased vaginal discharge, painful urination, bleeding between periods.
Many women may not have noticeable symptoms.
Complications:
If untreated, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy, and infertility in women. In men, it may lead to inflammation of the testicles.
Prevention and Treatment:
Safe sex practices, regular testing, and prompt treatment with antibiotics (usually ceftriaxone plus azithromycin). Drug resistance is rising, so proper medication is essential.
Imagine a youth in Enugu who starts having pain while urinating but avoids the hospital out of fear. By the time he seeks care, the infection has spread to his joints. Timely treatment could have prevented that.
Chlamydia
Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, this is often called the “silent” infection because it may show no symptoms—especially in women.
Symptoms:
Painful urination, unusual discharge, pain during sex, and lower abdominal pain.
Infections in men can cause pain and swelling in the testicles.
Complications:
Like gonorrhoea, it can lead to PID, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain if untreated.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Detected using nucleic acid tests (NAATs). Treated with antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin.
Think of a university student in Ibadan who feels fine but agrees to get tested during a health outreach. She tests positive for chlamydia and gets early treatment—protecting her fertility.
Syphilis
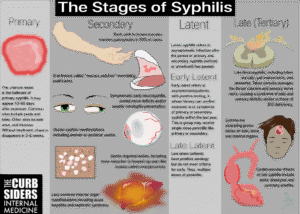
This is a more complex STI caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum. It develops in stages:
Primary: A painless sore (chancre) appears at the site of infection and heals on its own.
Secondary: Rash on palms and soles, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches.
Latent: No symptoms, but the infection remains in the body.
Tertiary: Can cause damage to the brain, heart, eyes, and other organs if untreated for years.
Transmission:
Through sexual contact or from mother to child during pregnancy.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Blood tests (e.g. VDRL or RPR) confirm infection. Treated with penicillin injections, which are very effective if caught early.
Think of a young pregnant woman in Jos who is tested during antenatal care and is found to have syphilis. Early treatment helps protect her unborn baby from congenital syphilis.
Summary
- Gonorrhoea and chlamydia often affect the reproductive system and can be silent, especially in women.
- Syphilis progresses in stages and can damage many parts of the body over time.
- All three are preventable and treatable with early diagnosis and appropriate antibiotics.
- Regular testing, safe sex, and health education are key to controlling their spread.
Evaluation
- Which STI is known as the “silent infection” and why?
- What are the four stages of syphilis?
- Why is early diagnosis important in the treatment of gonorrhoea?
The knowledge you’re gaining isn’t just for exams—it’s for life. You’re building the kind of insight that helps protect families, guide communities, and save lives. Keep your curiosity burning, and remember—Afrilearn is cheering you on every step of the way. See you in the next lesson!
