Back to: Inorganic Chemistry 100 Level
Welcome to class!
I’m so glad to see you again. Let’s begin with a picture from everyday life. Imagine two neighbours in Lagos shaking hands through their windows. Each person stretches out one hand, and when the hands meet, a connection is formed. In Chemistry, atoms also “stretch out” their orbitals to overlap with each other, and when this overlap happens, a chemical bond is formed. This simple but powerful idea is the basis of Valence Bond Theory (VBT).
Valence Bond Theory
What is Valence Bond Theory?
Valence Bond Theory explains how covalent bonds form when atomic orbitals from different atoms overlap. The electrons in these orbitals are shared, creating a stable bond.
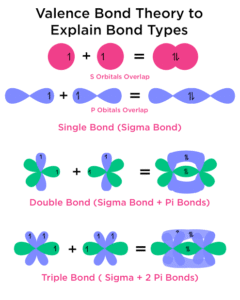
Key Ideas of Valence Bond Theory
Atoms form bonds by overlapping their half-filled orbitals.
The greater the overlap, the stronger the bond.
Each overlapping orbital contributes one electron, which pairs up to form a bond.
The shape of the molecule depends on the type of orbital overlap.
Types of Overlaps
1. Sigma (σ) Bonds
Formed by head-on (end-to-end) overlap of orbitals.
Stronger than π bonds.
Example: The single bond in H₂ is a sigma bond from the overlap of 1s orbitals.
Everyday link: Like two friends shaking hands directly face-to-face.
2. Pi (π) Bonds
Formed by sideways overlap of p orbitals.
Weaker than sigma bonds.
Always formed after a sigma bond.
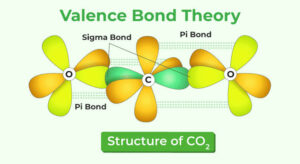
Example: In oxygen (O₂), there is one sigma and one pi bond.
Everyday link: Imagine two neighbours joining hands from the side window instead of directly.
Multiple Bond Formation
Single bond: One sigma bond.
Double bond: One sigma + one pi bond. Example: C=C in ethene.
Triple bond: One sigma + two pi bonds. Example: N≡N in nitrogen gas.
Strength of Bonds
Sigma bonds are stronger and more stable because the overlap is greater.
Pi bonds are weaker and more reactive.
Everyday Connections
The strength of sigma bonds explains why methane (CH₄) is stable enough to be used for cooking gas in Nigerian homes.
The presence of pi bonds in unsaturated fats (like vegetable oil) explains why they are more reactive than saturated fats (like butter).
The triple bond in nitrogen (N₂) makes it so stable that fertiliser industries in Nigeria require high energy to break it during ammonia production.
Summary
- VBT explains bond formation through orbital overlap.
- Sigma bonds = head-on overlap, stronger.
- Pi bonds = sideways overlap, weaker.
- Single = σ, Double = σ + π, Triple = σ + 2π.
Evaluation
- What is the main idea of Valence Bond Theory?
- Differentiate between sigma and pi bonds.
- State the types of bonds present in a double bond.
- Why is nitrogen gas (N₂) very stable according to VBT?
Fantastic work today! You’ve just learnt how atoms “shake hands” to form bonds. With Afrilearn, you are growing in confidence, making Chemistry simple, clear, and exciting. Keep this energy—your next lesson will open up even more wonders of bonding!
