Back to: CHEMISTRY SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the nature of matter. Enjoy the class!
NATURE OF MATTER
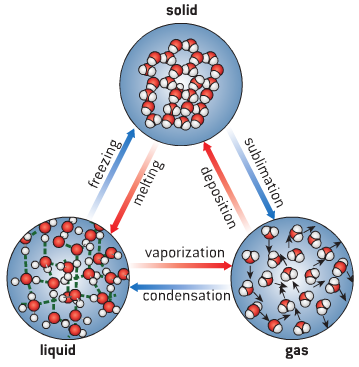
Matter is anything that has weight and occupies space. It exists in three states namely: solid, liquid and gas.
The fundamental difference between the three states of matter depends on the degree of movement of the particles they are made of.
SOLID STATE
The particles of a solid are tightly packed and held together by a strong electrostatic force.
The particles only vibrate to and fro about equilibrium or a fixed position. They have a definite shape and volume and very difficult to compress.
LIQUID STATE
The forces of attraction between molecules of liquids are weak compared to that of solids. Hence they have slight movements. This is why liquids can flow. They have a definite volume but not a definite shape.
GASEOUS STATE
As a result of the distance between the molecules of gases, the cohesive forces between them are very negligible and so they move randomly. Gases have no definite shape and volume. They assume the shape of the containing vessel.
EVALUATION
- What is matter?
- List and explain the three states of matter.
COMPARISON BETWEEN SOLID, LIQUID AND GAS

EVALUATION
- Define matter
- Compare the three states of matter in terms of (a) density (b) compressibility
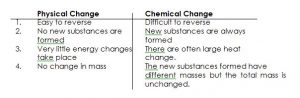
TYPES OF CHANGES
Whenever a given substance is heated, its state changes. There are two types of changes: physical and chemical.
PHYSICAL CHANGE:
A physical change is a change which is easily reversible and in which no new substances are formed. Examples are:
- Dissolution of common salt
- Changes in states of matter such as the melting of solids, freezing of liquids, evaporation of liquids, liquefaction of gases to solids, sublimation of solids.
- Magnetization and demagnetization of iron nails.
- Separation of a mixture by evaporation, distillation, fractional distillation etc.
EVALUATION
- What is a physical change?
- Give two examples of physical change.
CHEMICAL CHANGE:
A chemical change is a change which is not easily reversible and in which new substances are formed.
Examples of chemical change
- Rusting of iron/metals.
- Dissolution of metals and limestone in acids.
- Fermentation and decay of substances.
- Changes in electrochemical cells.
- The addition of water to quick lime.
- Burning of materials.
COMPARISON BETWEEN PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES
GENERAL EVALUATION/REVISION
- What is a chemical change?
- Give two examples of a chemical change.
- State three differences between physical and chemical changes.
- State the function of the following laboratory apparatuses: a) Fume cupboard b) Burette (c) Bunsen burner
READING ASSIGNMENT
- New School Chemistry for SSS by O.Y. Ababio. Pg 8 -9
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
- Which of the following changes is a chemical change? (a) melting of ice (b) liquefaction of air (c) slaking of lime (d) evaporation of a liquid
- Which of the following substances will occupy a wider space? (a)carbon (iv) oxide (b) liquid milk (c) pieces of chalk (d) water
- When a solid change to gas directly, this process is called (a) freezing (b) sublimation (c) Vaporization (d) evaporation
- Which of the following changes produces a new substance? (a) the reaction of water with sodium chloride (b) addition of acid to base (c) turning of margarine to oil (d) evaporation of water
- Which one of the following has a fixed shape and volume? (a) a cube of sugar (b) liquid wax (c) smoke (d) kerosene
THEORY
- Give two differences between physical and chemical changes.
- Give three processes, which involve a physical change
In our next class, we will be talking about Elements, Symbols and Valency. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

Thanks. I like it
Thanks. I love the classes
me too i love the class
What are the three state of matter
1 gas
2 solid
3 liquid.
What is matter?
Matter is anything that have weight or mass and occupy space.
it’s not weight or mass, it’s just mass. cause mass and weight are two diff things
Matter is anything that has weight and occupies space
matter is basically anything that has mass and occupies space
MATTER IS ANYTHING THAT HAS WEIGHT AND OCCUPY SPACE
matter is anything that has mass and can occupy space
I enjoyed the class. Tnks
Omor, the class dope😍
Matter is anything that has mass (not weight).
Thank you so much. The note was very helpful.
she’s correct dome
Wow the class was amazing thanks
What is mass
Thanks for giving time
I love this class
Matter is anything that has mass and occupy space
Between”piece of chalk, water, carbon dioxide, liquid milk” which one Will occupy wider space?
Thanks, very helpful.
wow 😲 this is so amazing I am just new to the class and I think I did not regret it thanks
We use the word “mass” because mass is an inheret properity of a substance, regardless the location or gravitational pull (this means that matter does not change regardless it location).
But eight is as a result of the pull of gravity on an object. eg on the moon an object will weigh less than thesame object on earth because of the gravitational force in earth is more. But mass is constant or does not change regardless the location
We use the word “mass” because mass is an inheret properity of a substance, regardless the location or gravitational pull (this means that matter does not change regardless it location).
But eight is as a result of the pull of gravity on an object. eg on the moon an object will weigh less than thesame object on earth because of the gravitational force in earth is more. But mass is constant or does not change.