Back to: MICROBIOLOGY 100 LEVEL
Welcome to class!
Hello, my brilliant friend! I’m truly glad you’re here again. You’ve been learning so much, and today’s topic is one that affects people all over the world—Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases. These are the diseases that surprise us, challenge our health systems, and remind us how important microbiology is in protecting lives.
Emerging And Re-emerging Diseases
What Are Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases?
Let’s break it down simply:
Emerging diseases are new diseases that were not known before, or diseases that are increasing very quickly in new places or among new groups of people.
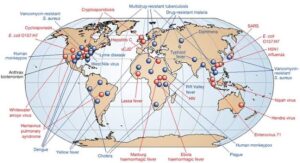
Re-emerging diseases are old diseases that had become less common but are now coming back—often stronger and more widespread than before.
These diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, or fungi. Some start in animals and then move to humans, especially when humans interact more with wildlife or disturb nature.
Examples of Emerging Diseases:
COVID-19 – Caused by the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), this disease started in 2019 and spread around the world. It was a new virus, and it affected millions globally, changing how we live and learn.
Ebola – This deadly viral disease first appeared in Central Africa. It spreads through contact with body fluids and has caused several outbreaks in West Africa.
Lassa fever – Common in parts of Nigeria and West Africa, this disease is caused by a virus spread by rats. It’s dangerous and sometimes deadly.
Zika virus – Spread by mosquitoes, it became a big concern when it was linked to birth defects in babies.
Examples of Re-emerging Diseases:
Tuberculosis (TB) – Even though we have treatments, TB is making a comeback, especially drug-resistant forms that don’t respond to normal medicine.
Measles – A vaccine-preventable disease that has returned in many areas due to low vaccination rates.
Cholera – Often re-emerges in places with poor sanitation and after natural disasters.
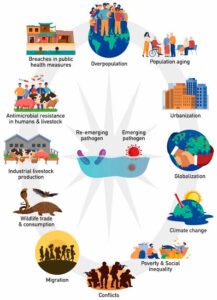
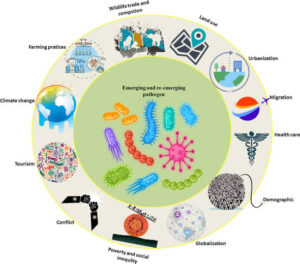
Why Do These Diseases Emerge or Re-emerge?
Climate change (more mosquitoes and insects spreading disease)
Deforestation (people getting exposed to new animal viruses)
Increased travel (a disease in one country can reach another in hours)
Poor health systems (makes it easy for diseases to spread)
Antibiotic resistance (some bacteria no longer respond to drugs)
Think of emerging diseases like a new thief in the neighbourhood, and re-emerging diseases like an old thief who was caught but escaped and came back—this time harder to catch! That’s why doctors, scientists, and even governments must always be ready.
Summary
- Emerging diseases are new or increasing diseases (e.g. COVID-19, Zika, Lassa).
- Re-emerging diseases are old diseases that are coming back (e.g. TB, measles).
- Causes include climate change, travel, poor health systems, and drug resistance.
- These diseases can spread quickly and affect global health.
Evaluation
- What is the difference between emerging and re-emerging diseases?
- Give two examples of emerging diseases.
- Mention two reasons why diseases re-emerge.
- Why is antibiotic resistance dangerous?
- What role can vaccination play in preventing re-emerging diseases?
Learning about diseases helps you protect yourself and your community. With Afrilearn by your side, you’re not just learning—you’re preparing to make the world a healthier, safer place. Keep going, great mind!
