Back to: Botany 500 Level
My brilliant Afrilearn Superstar, how body today?
I dey happy say you show face again because this lesson na serious matter wey join science, business, and fairness together. We dey talk about Bioprospecting and Benefit Sharing—two big terms wey sound like grammar but dey affect ordinary people like farmers, herbalists, and even your grandma wey sabi native herbs. Sit well, this gist go open your eyes to how we fit protect our rich African resources and still make everybody benefit from am.
Bioprospecting and benefit sharing
Imagine say one foreign scientist come your village, collect leaf from one plant your people don dey use to treat malaria for hundreds of years. Later, dem use that leaf to make medicine wey dey sell worldwide, but your village no hear from them again—not even small change. This kind situation dey very common, and e bring us to the matter of bioprospecting and benefit sharing.
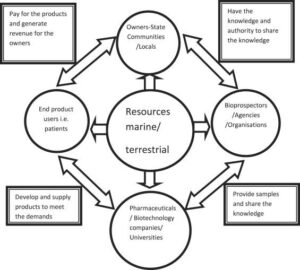
What is Bioprospecting?
Bioprospecting na the search for valuable compounds, genes, or traditional knowledge from plants, animals, and microbes—especially for making medicines, cosmetics, food, and industrial products.
Scientists and companies dey go places like forests, rivers, and communities with rich biodiversity (like Nigeria!) to find plants wey fit cure diseases or solve scientific problems.
Examples:
- Extracting compounds from Neem or Moringa for medicinal use.
- Using traditional knowledge about Aidan fruit (Tetrapleura tetraptera) for making herbal drinks or drugs.
- Searching mangrove plants in the Niger Delta for antibacterial agents.
Why Is It Important?
Bioprospecting help to:
- Discover new drugs and treatments (e.g., for cancer, malaria, diabetes).
- Improve agriculture with better plant varieties.
- Support scientific research using nature’s gifts.
But here’s the wahala: if people only collect resources and leave the local community empty-handed, e no make sense. That’s why Benefit Sharing matter well.
What Is Benefit Sharing?
Benefit sharing means making sure the people or communities who provide the biological resources or traditional knowledge get something in return—like money, infrastructure, royalties, jobs, or education.
Good Benefit Sharing Looks Like:
- Local farmers getting royalties when their crops or herbs are used in big products.
- Community health centres built by companies that used village plants.
- Giving credit to traditional knowledge holders, like herbalists or elders.
International Support: The Nagoya Protocol
Nigeria dey among countries wey support the Nagoya Protocol, a global agreement wey talk say people must get permission and share benefits when using genetic resources from other countries.

Challenges We Dey Face:
- Some companies dey exploit resources without consent (called biopiracy).
- Lack of awareness in communities about their rights.
- Weak local laws and enforcement.
Summary:
- Bioprospecting na the search for useful natural resources and knowledge, especially for medicine and science.
- Benefit sharing ensures communities are rewarded for their resources or traditional wisdom.
- Fairness, transparency, and respect are key to this process.
Evaluation:
- What is bioprospecting?
- Why is benefit sharing important?
- Mention one example of how benefit sharing can help a local community.
Your mind dey shine like morning sun. This kind knowledge no just help you pass exam, e go prepare you to stand for your community and make correct impact. Remember say for Afrilearn, we no just dey teach—we dey build future leaders like you. Keep your fire burning. More powerful lessons dey come your way!
