Back to: Botany 500 Level
Hello my Afrilearn champion! How far? I hope say you dey full of energy today as we continue this amazing learning journey. Today, we go talk about Conservation Strategies, which are ways we fit protect the amazing biodiversity wey dey our planet. There are two main strategies for conservation: in-situ and ex-situ. We go break them down today in a way wey you go love and easily understand. Let’s jump into it!
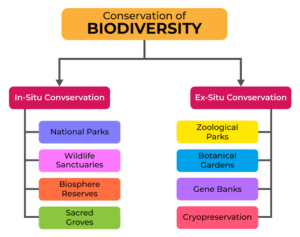
Conservation strategies (in-situ & ex-situ)
What Is Conservation?
Conservation na the effort to protect and preserve the natural world around us—plants, animals, ecosystems, and the environment. E get different ways we fit conserve biodiversity, and today we go focus on the two major strategies: in-situ and ex-situ. Both strategies help to keep species safe from threats like habitat loss, invasive species, and climate change.
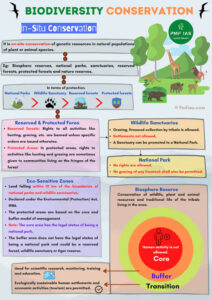
- In-Situ Conservation
In-situ conservation na when we conserve species in their natural habitat. This means say the species dey remain where they belong and are protected in the wild, without being moved to other locations. The goal of in-situ conservation na to maintain the balance of ecosystems and keep the species in the environment where they are most adapted to live.
Why e dey important?
In-situ conservation helps maintain the natural processes of ecosystems, such as the food web and plant pollination. By protecting natural habitats like forests, savannas, or wetlands, we ensure that animals and plants can continue to live in their natural environment. It also helps preserve the cultural and ecological integrity of the place, giving the species the best chance to survive in the long run.
Example:
In Nigeria, Yankari Game Reserve is an example of in-situ conservation. This reserve helps protect native species like elephants, lions, and various bird species by keeping them in their natural environment. The area is also managed to ensure that the species have access to the right food, water, and shelter they need.
- Ex-Situ Conservation
Ex-situ conservation involves conserving species outside their natural habitat. This is usually done when a species is at risk of extinction in the wild, or when their natural habitat has been destroyed. By removing the species from their environment and placing them in controlled settings, we can protect them and sometimes breed them to increase their numbers.
Why e dey important?
Ex-situ conservation provides a safe space for endangered species to thrive away from the dangers they face in the wild. It also helps breed species and reintroduce them into their natural habitat when the environment is safe again. Ex-situ methods like zoos, botanical gardens, and seed banks play a critical role in saving species from extinction.
Example:
One example of ex-situ conservation is the Nigerian National Zoological Garden in Abuja. They care for endangered species like the West African lion, African grey parrots, and hippopotamuses. By breeding these animals in a controlled environment, the zoo helps increase their population and, in the future, might reintroduce them back into the wild.
Another example is the seed banks wey dey store the seeds of important plants, in case something happens to their natural habitat. If a species of plant becomes endangered, the seeds stored in the bank can be used to grow new plants and reintroduce them into the wild.
Comparison of In-Situ and Ex-Situ Conservation
- In-Situ Conservation:
- Species are conserved in their natural environment.
- Helps maintain the balance of ecosystems.
- Best for species that still have a chance of survival in the wild.
- Examples include national parks, reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries.
- Ex-Situ Conservation:
- Species are conserved outside their natural habitat.
- Provides protection from immediate threats like poaching or habitat destruction.
- Best for species that are critically endangered or have lost their natural habitat.
- Examples include zoos, botanical gardens, and seed banks.
Why Are Both Strategies Important?
Both in-situ and ex-situ strategies are important for conservation. While in-situ helps maintain the natural balance and allows species to continue to live in the wild, ex-situ provides a safety net for species that need extra care and protection outside their natural environment. Sometimes, a combination of both strategies is used to ensure the survival of a species.
Summary:
- In-situ conservation protects species in their natural habitat, helping to maintain ecosystem balance.
- Ex-situ conservation protects species outside their natural habitat, often in zoos, botanical gardens, or seed banks.
- Both strategies are important for the survival of species and the protection of biodiversity.
Evaluation:
- What is the difference between in-situ and ex-situ conservation?
- Give one example of in-situ conservation and one example of ex-situ conservation.
- Why is it important to use both in-situ and ex-situ conservation methods?
You’re doing amazing, my Afrilearn superstar! I’m so proud of how you’re soaking in all this information. Today, you’ve learned two major ways we can help protect our planet’s precious biodiversity—in-situ and ex-situ conservation. Remember, every small action counts in protecting the environment, and now you know how these strategies play a huge part in saving species from extinction. Keep shining, stay awesome, and get ready for the next lesson. You’re a true champion!
