Back to: Botany 500 Level
My Afrilearn superstar, how you dey today?
I dey happy say you don come back for another interesting lesson! Today we go reason about something wey dey critical for any study, especially when you dey work with plants, people, or the environment. We dey talk about Data Collection and Analysis. This topic no just dey important for your studies but na the key to understanding anything wey you wan solve or improve. Abeg, come close, because this one go give you the power to turn raw information into real knowledge!
Data collection and analysis
You don ever gather information before? Maybe you wan learn how farmers in your village dey plant crops or how people use herbs for medicine. The first step na to gather the information—that’s data collection. After you gather am, the next step na to organise and understand am well—that’s data analysis. These two steps na the backbone of every research work. Without them, no way to know if you’re solving the right problem or making progress.
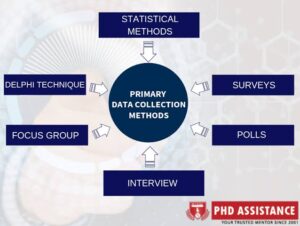
What is Data Collection?
Data collection na the process of gathering information from different sources in a systematic way. For you to get correct results, the information must be accurate, relevant, and complete.
Types of Data Collection Methods:
- Qualitative Data Collection: This one focuses on understanding people’s opinions, beliefs, or experiences. It’s mostly non-numerical and based on interviews, observations, and surveys.
- Example: You interview village herbalists about how they prepare medicinal plants.
- Quantitative Data Collection: This one focuses on gathering numerical data that can be counted or measured. It’s about facts and figures.
- Example: You survey farmers to find out how many kilograms of cassava they harvest yearly.
Methods of Data Collection:
- Interviews (like we discussed earlier)
- Surveys and Questionnaires
- Observations (watching how something happens)
- Experiments (testing something in a controlled way)
- Secondary Data (using data already collected by others, like government reports)
What is Data Analysis?
Once you’ve collected your data, the next step is to make sense of it—this na data analysis. Data analysis helps you find patterns, relationships, or trends in the data. It helps you know if your research question has been answered.
Types of Data Analysis:
- Qualitative Analysis:
This involves interpreting non-numerical data. You look for patterns, themes, or common answers from interviews or discussions.- Example: After interviewing several farmers, you might notice many of them use the same method for planting cassava.
- Quantitative Analysis:
This involves using numbers to analyse data. You calculate averages, percentages, and compare results.- Example: If you survey 100 people and 80 of them say they use local herbs, you can calculate that 80% of the people use local herbs.
Tools for Data Analysis:
- Statistical Software: For example, Excel, SPSS, or Google Sheets. These tools help you do calculations, make graphs, and analyse trends.
- Coding (for qualitative data): Organising and tagging responses from interviews or surveys into themes or categories.
Steps in Data Collection and Analysis:
- Plan Your Data Collection:
Decide what data you need and how you will collect it. Is it through interviews? Surveys? Observations? - Collect the Data:
Go out, interview people, observe, or distribute your surveys. Make sure the data is accurate and reliable. - Organise the Data:
Put the data in a way that makes sense. If it’s numbers, arrange them in tables. If it’s text, group similar ideas together. - Analyse the Data:
Look for patterns or insights. Use statistics or qualitative methods to break down the information. - Interpret the Results:
What do your findings mean? Does your data support your original hypothesis or answer your research question?
Summary:
- Data collection is the process of gathering information in a systematic way.
- It can be qualitative (focused on experiences and opinions) or quantitative (focused on numbers and measurements).
- Data analysis helps you understand the meaning behind the data. It involves finding patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Tools like surveys, interviews, and software help with both collection and analysis.
Evaluation:
- What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data collection?
- Why is data analysis important after data collection?
- Give one method of qualitative data collection and one method of quantitative data collection.
With this knowledge, you be a true researcher in the making. Data is power, and you now have the key to unlock insights that can change your world. Keep shining, keep learning—Afrilearn dey your back every step of the way! More exciting lessons dey come your way soon!
