Back to: PHYSICS SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about electric charges. Enjoy the class!
Electric Charges
Production of electric charges
The experimental discovery shows that whenever two bodies are rubbed together, they acquire attracting property on some light objects such as paper. Consider one ebonite rod rubbed with a fur; they are seen to attract each other. The two bodies are said to be electrified. Other examples are glass and silk.
Types of charges
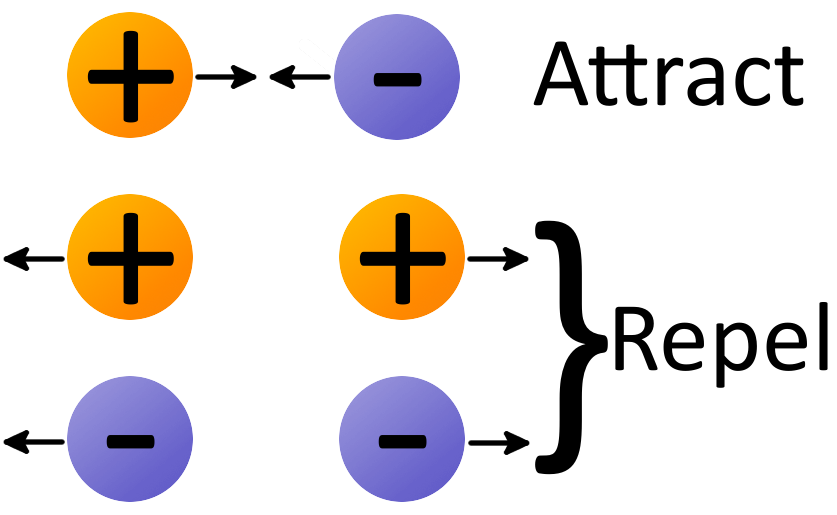
There are two types of charges
- Positive charge and
- Negative charge
A glass rod is said to acquire positive (+ve) charge while ebonite acquires negative (-ve) charge. The law of electrostatic states that likes charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other.
Charging of electric charges
Charging of electric charges can be done through the following means:
- Charging by electrostatic induction
- Charging by friction
Charging by electrostatic induction:
Electrostatic induction is a method of charging a body by introducing a charged body to a neutral body. When this is done, the body is said to be induced with a charge.
To charge a body, the neutral body A is made to stand on an insulator, not on a conductor. A charged body B is introduced to the neutral body of A by electrostatic induction. The nearer side of A gets reversely charged while the further side gets similarly charged.
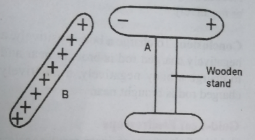
When the charged body B is removed, the induced positive and negative charges are neutralized, showing no resultant charge.
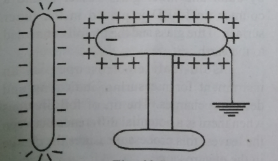
When the body is touched, the positive charge flows to the earth through the hand but the negative charge does not flow to the earth.
If the hand is removed first, and then rod B is introduced, the whole surface will be bound with a negative charge.
The neutral body can be charged either positively or negatively.
In conclusion:
To charge a body positively, a negatively charged rod is brought near and to charge a body negatively, a positively charged rod is brought near.
Charging by friction:
Two substances such as glass and silk, when rubbed together, become electrically charged. During rubbing, some electrons are transferred from the glass to the silk. The silk acquires a net negative charge (excess electrons) while the glass acquires a net positive charge (electron deficit). If ebonite (hard rubber) is rubbed with fur, the ebonite is negatively charged and the fur is positively charged. A body with a positive charge attracts one with a negative charge but repels one with a positive charge, i.e. like charges repel, unlike charges attract.
Distribution of charges on conductors
Experimental works have shown that charges are distributed where there is a sharp curve. The density of these charges is greater at the surface of a sharp curve. The charge per unit area of a charged surface is called surface density.
Surface density is greater at the corner or pointed edge than at the plain surface.
Storage of charges
Electrophorus:
The electrophorus is a device for transferring and storing charges. It produces electric charges by electrostatic induction or by friction.
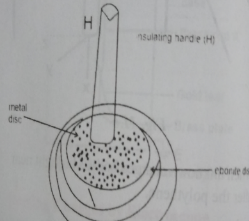
Electrophorus
Capacitor:
A capacitor is a device for storing electrical charges. It consists of two conductors which are parallel to each other. The storage of a capacitor is increased due to an increase in its conductivity.
In our next class, we will be talking about Gold Leaf Electroscope. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
