Back to: Botany 500 Level
My dear Afrilearn star, how you dey today?
I dey happy to see say you still dey show up with that hunger for knowledge! Today, we go talk about Ethnobotanical Case Studies, and I know say this topic go fire your brain because na the sweet combination of plants, culture, and real-life application. Grab your pen, because we dey about to dig deep into how traditional knowledge of plants dey play a big role in people’s lives and how scientists dey use am for research.
Ethnobotanical case studies
Every day, for the small villages, cities, and towns across Nigeria, people use plants for food, medicine, building materials, and even spiritual practices. This knowledge no just come from textbooks—it come from years of experience and deep connection with nature. The science wey study how people use plants for these purposes na Ethnobotany. When we talk about ethnobotanical case studies, we dey look at real examples of how different communities use plants, how this knowledge dey passed down, and how it benefits both the people and science. Let’s see how this knowledge dey work!

What Are Ethnobotanical Case Studies?
Ethnobotanical case studies na real-life examples wey researchers use to study how people interact with plants in their environment. These studies help us understand the cultural, medicinal, agricultural, and spiritual roles of plants. Through these studies, researchers can document plant species, how they are used, and why they are important to a particular group of people.
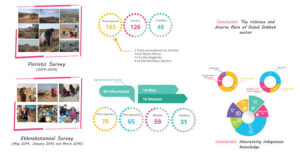
Case Study 1: The Use of Bitter Leaf in Nigeria
In many Nigerian communities, bitter leaf (Vernonia amygdalina) na important plant wey people dey use for both medicinal and culinary purposes. From the Yoruba people to the Igbo and Hausa, bitter leaf dey used to treat malaria, high blood pressure, and even stomach ailments.
- Cultural Importance: Bitter leaf is also used in spiritual rituals by some communities to cleanse negative energy.
- Ethnobotanical Research: Researchers have documented how local herbalists extract the juice from bitter leaf to make a remedy for fever. This traditional practice has now attracted the attention of modern medicine, and some scientists are studying how the chemical compounds in the leaf can be used in anti-malarial drugs.
Case Study 2: The Role of Neem Tree (Azadirachta indica)
The neem tree is well-known across Nigeria and many parts of Africa for its wide range of uses. From its leaves, seeds, and bark, different parts of the neem tree are used for both medicinal and agricultural purposes.
- Medicinal Use: Local communities use neem leaves to treat fever, skin diseases, and as an anti-parasitic agent. In some areas, neem is also used to prepare a natural pesticide to protect crops from insects.
l - Cultural Importance: In some communities, neem trees are planted around the home for protection against evil spirits and pests.
- Ethnobotanical Research: Scientists are studying the potential of neem as an eco-friendly pesticide, and some are working on creating neem-based products for the global market. This case study highlights the deep connection between local people and the environment, while also showing how this knowledge is being integrated into modern agricultural and pharmaceutical industries.
Case Study 3: The Use of Shea Tree (Vitellaria paradoxa)
The sheanut from the shea tree is not only important in African cuisine but also has economic significance in the production of shea butter, which is used in cosmetics, skincare, and even as a cooking fat.
- Economic and Cultural Use: Shea butter is made by women in many rural Nigerian communities, and it plays a huge role in their livelihoods. In addition to being a key product in local markets, it is used for treating dry skin and making traditional beauty products.
- Ethnobotanical Research: Researchers are investigating the chemical properties of shea butter to improve its use in modern skin-care products. There’s also an increasing interest in sustainable harvesting methods to protect the shea tree from overexploitation.
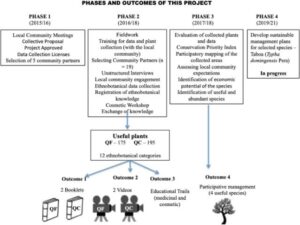
Case Study 4: The Role of Moringa (Moringa oleifera)
Moringa is one of the most researched plants worldwide for its nutritional and medicinal benefits.
- Medicinal and Nutritional Use: Moringa leaves are rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins. People use it to treat malnutrition, inflammation, and to boost immune systems.
- Ethnobotanical Research: In some Nigerian communities, moringa leaves are used as a supplement for children’s diets. Modern research is now confirming these traditional uses and exploring how moringa can help in the fight against malnutrition and even chronic diseases like diabetes.
Summary:
- Ethnobotanical case studies show how plants are used in real life by different communities for medicine, food, and cultural practices.
- These studies help us understand the deep connection people have with plants and how traditional knowledge contributes to modern science.
- Case studies from Nigeria, like the use of bitter leaf, neem, shea, and moringa, showcase how plants shape local culture and can offer solutions to modern problems.
Evaluation:
- What is an ethnobotanical case study?
- Name two plants mentioned in the case studies and their uses.
- Why is ethnobotanical research important for modern medicine and agriculture?
You dey make us proud, and with every lesson you take in, you dey unlock another level of greatness. Keep up the great work, and I can’t wait to see how you go take this knowledge to new heights! More amazing lessons dey on the way—let’s keep this journey going strong!
