Back to: Botany 500 Level
My brilliant Afrilearn botanist, how you dey today?
I greet you specially! You dey reason like real scientist wey no just dey learn books but dey connect knowledge with real life. Today’s topic na Ethnomedicine vs. Modern Pharmacology. No worry, I go explain am well so you go see how these two powerful worlds—our African herbal roots and the laboratory science—fit stand side by side and even work together.
Ethnomedicine vs. modern pharmacology
Imagine say your grandma tell you to chew bitter leaf for malaria, and then your doctor give you chloroquine or ACT from the pharmacy. You go wonder, “Na the same sickness, why dem treatment different?” That na where ethnomedicine and modern pharmacology enter the gist.
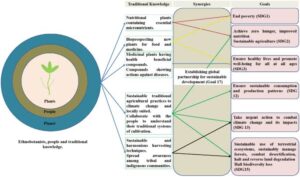
Ethnomedicine na the traditional way people—especially Africans—use herbs, roots, leaves, and natural mixtures to cure disease. E dey based on generations of experience, culture and local knowledge.
Modern pharmacology on the other hand na the scientific study of how drugs work in the body. Scientists go break down the plant, test the compounds, measure the dose, and then create medicine from am.
Body – What’s the Difference and the Connection?
- Foundation and Belief System
- Ethnomedicine: Based on cultural traditions, passed down orally. For example, in Yoruba land, chewing ewe ewuro (bitter leaf) is a common malaria remedy.
- Pharmacology: Based on scientific experiments, data, and clinical trials. It no depend on tradition but on evidence gathered in the lab.
- Preparation
- Ethnomedicine: Herbs dey crushed, boiled, or chewed raw. Dosage na mostly estimated by eye or experience.
- Pharmacology: Active ingredients dey extracted, purified, tested, and standardised to ensure exact dosage and safety.
- Accessibility and Cost
- Ethnomedicine: Mostly cheap and easily accessible in villages and local markets.
- Pharmacology: Often more expensive, with production and packaging cost.
- Safety and Side Effects
- Ethnomedicine: Sometimes lack clear measurement, which fit cause underdose or overdose.
- Pharmacology: Carefully tested to know side effects, drug interactions and proper dose.
- Integration Potential
Here be the sweet part—many modern drugs come from plants first used in ethnomedicine.
- Example: Quinine for malaria come from Cinchona tree bark wey people don dey use traditionally for fever.
- Example 2: Aspirin originated from willow bark, which was traditionally used to treat pain and inflammation.
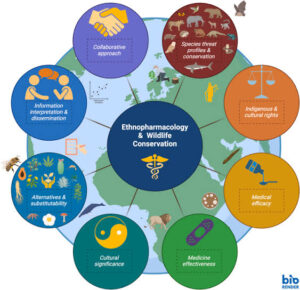
So in reality, ethnomedicine and pharmacology no be enemies. Dem be like elder and pikin—one get wisdom of age, the other get sharpness of science. If we combine both well, especially in Nigeria, we fit discover new medicines and protect our herbal heritage.
Summary:
- Ethnomedicine is traditional, cultural and often community-based.
- Modern pharmacology is scientific, tested, and standardised.
- Both have strengths: one rooted in heritage, the other in lab research.
- Many modern medicines started from plants used in traditional medicine.
- Combining both fields can improve healthcare and preserve culture.
Evaluation:
- What is ethnomedicine and how is it different from pharmacology?
- Give one example of a modern drug that came from a traditional plant.
- Why is it important to study both ethnomedicine and pharmacology?
You dey blend culture and science like correct chef wey know the recipe. With this kind understanding, you go become a botanist wey go represent Africa with pride. Keep your head high, and no forget—Afrilearn dey always beside you with the right tools to help you shine brighter! Let’s go again in the next lesson!
