Back to: PHYSICS SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the gold-leaf electroscope. Enjoy the class!
Gold Leaf Electroscope

This is an instrument used to detect if a body carries an electric charge and the type of charge.
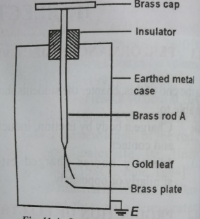
Gold leaf electroscope
To detect if a body is charged
To detect if a body is charged, we use it to charge the gold-leaf. To charge the electroscope by induction, take the following steps.
- Bring a charged object near the metal cap.
- While the object is still close by, earth the cap by touching it momentarily.
- After breaking the earth connection, withdraw the object of the charge.
- The metal rod and the gold-leaf acquire the same charge which is opposite to that on the charging object. The leaf diverges (like charges repel)
Note that the electroscope can also be charged by direct contact. This is done by placing a charged body on the metal cap of the electroscope.
To determine the sign of an unknown charges
- Charge the electroscope by induction causing the leaf to diverge.
- Bring the unknown charged body close to the cap of the electroscope.
- If the charge has the same sign as that on the electroscope, the leaf diverges further.
- If the charge is opposite to that on the electroscope, the leaf collapses.
Note that the same will happen if an uncharged body is brought near the cap.
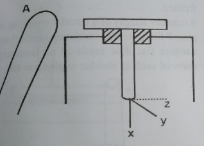
Charging distribution on conductor
Any excess electric charge on a conductor resides on the surface, and not inside the conductor. For a uniformly curved surface such as a sphere, the charge is distributed uniformly on the surface
For a conductor with sharp edges, the charges are concentrated on the sharpest point
Lightning and lightning conductor
We often see the lightning flash and hear the rumbling sound of thunder when it is raining or during a thunderstorm. Though both occur at the same time, we see lightning before hearing the sound of the thunder. This is because light travels much faster than sound. Lightning is caused by a storm cloud which is highly charged as a result of the rubbing action between the cloud and the air. Lightning normally strikes a tall building, when this happens; the electric charge is conducted through the building to the earth causing considerable damage to its structure. A lightning conductor consists of a copper strip with a sharply pointed end (or spikes) projecting above the building to be protected while the lower end is connected to a metal plate buried in the ground.
The action of the lightning conductor
To protect a building from the damaging action of lightning, we use a lightning conductor. If a positively charged cloud passes over the building, electrons are attracted from the earth to the tip of the lightning conductor. The electrons gradually leak from the top into the cloud where the positive charges are quickly neutralized. A large amount of heat generated can also cause severe burns.
In our next class, we will be talking about Field. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
