TOPIC: METALLIC BONDING
CONTENT
- Properties, Factors affecting the formation of metals
- Inter molecular bonding
- Vander-walls forces and hydrogen bonds
- Composition and Uses.
Metallic Bonding
The atoms of metals are held together in crystal lattice by metallic bonds
Properties
- they are good conductors of electricity and heat
- high melting and boiling points
- they are malleable and ductile
- they ionize by loosing electrons
Factors affecting the formation of metal strength
The Valence Electrons
Intermolecular Bonding
This is the type of chemical bonding which can be found in some molecular solid. Examples of intermolecular forces are
- vander walls forces
- Hydrogen force/bond
Vander Waal Forces: this is the weak attractive forces that exist between the molecule.
Importance of Vander waal forces
- it is important in the liquefaction of gases
- it is used in the formation of molecular lattices like iodine and naphthalene crystals.
EVALUATION
- State the properties of the following bonds.
- metallic bond b. Vander waal
- Give the diagram of a named metallic element (bonding diagram)
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding occur when hydrogen is covalently bonded with strongly electronegative element e.g nitrogen, fluorine, oxygen.
These electronegative elements pall the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bonds toward themselves. Thus it results in dipole where the hydrogen is positive and the electronegative element is negative.
An electrostatic attraction set up when the positive pole of one molecule attract the negative pole of another molecule.
NB: The attractive force that exist between the two poles is called hydrogen bond.
Example of hydrogen bond
- Hydrogen fluoride molecules
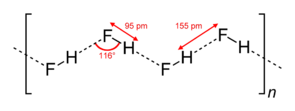
- Water molecules (ice crystal)

NB: There is covalent bond in a molecule of water while hydrogen bond is formed in molecules of water.
Use
It helps in the formation of water, alkanols and some organic acid molecules
GENERAL EVALUATION
- Use diagram to differentiate between a molecule of water and molecules of water
- State the molecules of a substance with strongest hydrogen bond.
- Explain simple cubic structure
READING ASSIGNMENT
New School Chemistry by O.Y Ababio pg 294-298
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
- An example of intermolecular bonding is (a) Vander wall (b) metallic (c) ionic (d) covalent
- Both metallic substance and electrovalent compound are similar because (a) Both dissolve readily in water. (b) they have low melting point. (c) they can conduct electricity. (d) they have low boiling point.
- The dotted line in an intermolecular bond stands for ____ (a) oxygen (b) hydrogen bond (c) ionic bond (d) covalent bond
- Vander Wall force of attraction can be grouped as (a) Strongest force (b) hydrogen bond
(c) weakest force (d) ionic bond.
- Metallic bond can easily be identified by the presence of (a) positive charge (b) negative charge (c) neutral charge (d) double bonds.
THEORY
- State the type of chemical bond found in the following substances
- Magnesium
- Sodium chloride
- Ammonium chloride
- Molecules of hydrogen fluoride
- A molecule of hydrogen
- State four properties of the following chemical bonds:
- Electrovalent bond
- covalent bond
- dative bond
- hydrogen bond
- metallic bond
