Back to: Botany 500 Level
My sharp and steady Afrilearn learner, how your side dey today?
I dey very happy say you still dey waka this learning journey with better zeal. Today, we go discuss another gbedu topic wey dey very important if you wan understand how medicinal plants really work—Methods of Preparation and Administration. You fit get the correct leaf or root, but if you no sabi how to prepare or use am, e no go work well. So let’s yarn like padi and break am down proper.
Methods of preparation and administration
For our different towns and villages across Nigeria, if you ask any herbalist or elderly person, dem go tell you say “no be only the leaf wey cure person, na how you take use am”. That’s true talk. The way we prepare and administer herbal medicine na the key to whether e go cure, work small, or even cause wahala. That’s why you as a Botany student must understand the correct methods wey fit preserve the healing power and avoid harm.
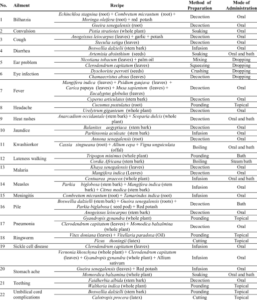
Body – Common Methods of Preparation
- Infusion
This na when you soak soft plant parts like leaves or flowers in hot water, like tea.
- Example: Scent leaf for cough—you pour hot water on the leaf, leave am for some minutes, then drink the liquid.
- Easy and effective for delicate herbs.
- Decoction
This one involve boiling hard plant parts like roots, bark, or seeds for a longer time to bring out the active ingredients.
- Example: Dogoyaro (neem) leaf or bark—boiled for malaria.
- Strong and bitter, but very effective.
- Maceration
Here, the plant material dey soaked in cold or room temperature water for hours or even days.
- This method dey used when heat fit spoil the active ingredient.
- Pounding or Grinding
This one involve crushing fresh herbs into paste or powder.
- Example: Aloe vera gel dey extracted by slicing and scooping.
- Powdered ginger or turmeric dey used in this way too.
- Fermentation
In some cases, herbs dey soaked and left to ferment small before use.
- Example: Some traditional mixtures for digestive issues.
- Burning or Smoking
Some herbs dey burned and the smoke inhaled.
- Example: Dry herbs for spiritual or respiratory cleansing.
Methods of Administration (How Dem Dey Take Am)
- Oral (By Mouth)
This na the most common—drinking as tea, chewing, or swallowing powder.
- Example: Bitter leaf juice for malaria.
- Topical (For Skin)
Rubbing paste, oils or gel on the skin.
- Example: Aloe vera on burns, or ground neem for rashes.
- Inhalation
Inhaling steam or smoke from prepared herbs.
- Example: Steaming with scent leaf for blocked nose.
- Bathing or Soaking
Herbs dey added to water wey person use bath.
- Example: Bathing with medicinal leaves for skin problems.
- Enema or Suppository
Less common but some communities use it traditionally for cleansing.
Why This Matter
- Correct preparation keep the medicinal properties intact.
- Wrong method fit reduce power or even make it harmful.
- Good administration ensures it reaches the part of the body wey need am.
- As a future scientist, this knowledge go help you in research, preservation, and even health advice.
Summary:
- Herbal medicines get different preparation methods: infusion, decoction, pounding, fermentation and more.
- Methods of taking them include drinking, rubbing, inhaling, and bathing.
- Proper preparation and administration na the key to getting full benefit without side effects.
Evaluation:
- What is the difference between infusion and decoction?
- Mention two ways medicinal plants can be administered.
- Why is it important to prepare herbal medicine correctly?
As you continue to learn about plants and medicine, always remember say your knowledge fit bring healing and help preserve our African heritage. Keep shining, keep learning, because for Afrilearn, na your success be our pride. On to the next one, genius!
